Comparative Genomics of Limosilactobacillus reuteri YLR001 Reveals Genetic Diversity and Probiotic Properties
- PMID: 39203478
- PMCID: PMC11356486
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12081636
Comparative Genomics of Limosilactobacillus reuteri YLR001 Reveals Genetic Diversity and Probiotic Properties
Abstract
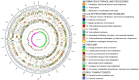
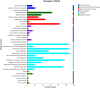
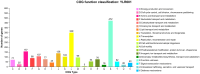
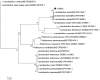
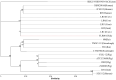
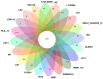
To gain deeper insights into the genomic characteristics of Limosilactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) YLR001 and uncover its probiotic properties, in the current study, a comprehensive analysis of its whole genome was conducted, explicitly exploring the genetic variations associated with different host organisms. The genome of YLR001 consisted of a circular 2,242,943 bp chromosome with a GC content of 38.84%, along with three circular plasmids (24,864, 38, 926, and 132,625 bp). Among the 2183 protein-coding sequences (CDSs), the specific genes associated with genetic adaptation and stress resistance were identified. We predicted the function of COG protein genes and analyzed the KEGG pathways. Comparative genome analysis revealed that the pan-genome contained 5207 gene families, including 475 core gene families and 941 strain-specific genes. Phylogenetic analysis revealed distinct host specificity among 20 strains of L. reuteri, highlighting substantial genetic diversity across different hosts. This study enhanced our comprehension of the genetic diversity of L. reuteri YLR001, demonstrated its potential probiotic characteristics, and established more solid groundwork for future applications.
Keywords: Limosilactobacillus reuteri; complete genome sequencing; probiotic properties; yak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zheng J., Wittouck S., Salvetti E., Franz C.M.A.P., Harris H.M.B., Mattarelli P., O’toole P.W., Pot B., Vandamme P., Walter J., et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020;70:2782–2858. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004107. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ortiz-Rivera Y., Sánchez-Vega R., Gutiérrez-Méndez N., León-Félix J., Acosta-Muñiz C., Sepulveda D.R. Production of Reuterin in a Fermented Milk Product by Lactobacillus reuteri: Inhibition of Pathogens, Spoilage Microorganisms, and Lactic Acid Bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2017;100:4258–4268. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11534. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

