Exploration of the Muribaculaceae Family in the Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Metabolism, and Function
- PMID: 39203797
- PMCID: PMC11356848
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16162660
Exploration of the Muribaculaceae Family in the Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Metabolism, and Function
Abstract
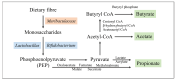
The gut microbiota are mainly composed of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes and are crucial for metabolism and immunity. Muribaculaceae are a family of bacteria within the order Bacteroidetes. Muribaculaceae produce short-chain fatty acids via endogenous (mucin glycans) and exogenous polysaccharides (dietary fibres). The family exhibits a cross-feeding relationship with probiotics, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. The alleviating effects of a plant-based diet on inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes are associated with an increased abundance of Muribaculaceae, a potential probiotic bacterial family. This study reviews the current findings related to Muribaculaceae and systematically introduces their diversity, metabolism, and function. Additionally, the mechanisms of Muribaculaceae in the alleviation of chronic diseases and the limitations in this field of research are introduced.
Keywords: Muribaculaceae; chronic diseases; gut microbiota; polysaccharides; short-chain fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim H., Caulfield L.E., Garcia-Larsen V., Steffen L.M., Coresh J., Rebholz C.M. Plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of incident cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular disease mortality, and all-cause mortality in a general population of middle-aged adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e012865. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012865. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases