Compliance with a Healthful Plant-Based Diet Is Associated with Kidney Function in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 39203885
- PMCID: PMC11356780
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16162749
Compliance with a Healthful Plant-Based Diet Is Associated with Kidney Function in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
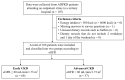
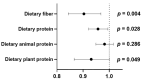
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a genetic kidney disorder with multiple cyst formation that progresses to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage kidney disease. Plant-based diets have attracted considerable attention because they may prevent CKD development. This study investigated whether adherence to a plant-based diet is associated with kidney function in patients with ADPKD. The overall plant-based diet index (PDI), healthful PDI (hPDI), and unhealthful PDI (uPDI) were calculated using dietary intake data. Among 106 ADPKD patients, 37 (34.91%) were classified as having advanced CKD (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2). The overall PDI and hPDI were lower, but the uPDI was higher in patients with advanced CKD than in those with early CKD. The hPDI was negatively correlated with the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio. Moreover, the hPDI was inversely associated with advanced CKD [odds ratio (OR): 0.117 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.039-0.351), p < 0.001], and the uPDI was positively associated with advanced CKD [OR: 8.450 (95% CI: 2.810-25.409), p < 0.001]. The findings of the current study demonstrate that greater adherence to a healthful plant-based diet is associated with improved kidney function in ADPKD patients.
Keywords: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; plant protein; plant-based diet; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Chebib F.T., Zhou X., Garbinsky D., Davenport E., Nunna S., Oberdhan D., Fernandes A. Tolvaptan and Kidney Function Decline in Older Individuals with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials and Observational Studies. Kidney Med. 2023;5:100639. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

