A Fixed Combination of Palmitoylethanolamide and Melatonin (PEATONIDE) for the Management of Pain, Sleep, and Disability in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 39203921
- PMCID: PMC11357461
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16162785
A Fixed Combination of Palmitoylethanolamide and Melatonin (PEATONIDE) for the Management of Pain, Sleep, and Disability in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Pilot Study
Abstract
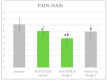
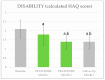
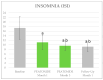
Fibromyalgia is characterized by chronic widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. Recent theories attribute fibromyalgia to central sensitization syndromes, suggesting altered nociceptive processing leads to hyperalgesia and allodynia. Standardized effective treatments are currently lacking. Palmitoylethanolamide and melatonin have shown pain-relieving effects in chronic pain conditions, including fibromyalgia, with excellent safety. Our open-label study assessed the impact of a daily combination of 1200 mg of palmitoylethanolamide and 0.2 mg of melatonin on pain, sleep, and quality of life in fibromyalgia patients. Between June 2023 and March 2024, 50 patients (2016 ACR criteria) were treated and evaluated at baseline, 1 month, 3 months, and 4 months (1 month discontinuation). The assessments included VAS for pain, ISI for insomnia, HAQ for health assessments, and a tender points evaluation. The patients, averaging 54.12 years old with a 3:1 female-to-male ratio, showed significant improvements in VAS, ISI, and HAQ scores relative to their own baselines and a reduction in tender points at 1 and 3 months, which was maintained at 4 months. No adverse events were reported. This study is the first to demonstrate the efficacy of a palmitoylethanolamide and melatonin combination as an adjunct therapy in fibromyalgia, highlighting its potential to reduce pain and improve sleep and quality of life.
Keywords: fibromyalgia; melatonin; nutraceuticals; pain; palmitoylethanolamide; quality of life; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide (um-PEA) as Add-on Treatment in Fibromyalgia Syndrome (FMS): Retrospective Observational Study on 407 Patients.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(4):326-333. doi: 10.2174/1871527318666190227205359. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30827269
-
The effect of melatonin in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study.Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19(1):9-13. doi: 10.1007/s100670050003. Clin Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 10752492 Clinical Trial.
-
PRECISE trial (Pain RElief Combination Intervention StratEgies): protocol for the clinical trial of a pregabalin-melatonin combination for fibromyalgia.BMJ Open. 2024 Jun 23;14(6):e087180. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087180. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38910006 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin in the treatment of fibromyalgia symptoms: A systematic review.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 Feb;38:101072. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2019.101072. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 31783341
-
Treatment of drug-resistant fibromyalgia symptoms using high-intensity laser therapy: a case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Mar;38(3):517-523. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3856-5. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29080932 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive Dysfunction in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome-Aetiology and Potential Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 22;26(5):1896. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051896. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Juvenile Primary Fibromyalgia Syndrome: Advances in Etiopathogenesis, Clinical Assessment and Treatment: A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2025 May 10;13(5):1168. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051168. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ben-Yosef M., Tanai G., Buskila D., Amital D., Amital H. Fibromyalgia and Its Consequent Disability. [(accessed on 1 April 2024)];IMAJ Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2020 22:446–450. Available online: https://www.ima.org.il/MedicineIMAJ/viewarticle.aspx?year=2020&month=07&.... - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F., Smythe H.A., Yunus M.B., Bennett R.M., Bombardier C., Goldenberg D.L., Tugwell P., Campbell S.M., Abeles M., Clark P., et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia: Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1990;33:160–172. doi: 10.1002/ART.1780330203. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

