Development and Application of Automated Sandwich ELISA for Quantitating Residual dsRNA in mRNA Vaccines
- PMID: 39204025
- PMCID: PMC11359411
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12080899
Development and Application of Automated Sandwich ELISA for Quantitating Residual dsRNA in mRNA Vaccines
Abstract
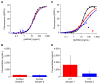
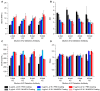
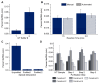
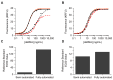
The rise of mRNA as a novel vaccination strategy presents new opportunities to confront global disease. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is an impurity byproduct of the in vitro transcription reaction used to manufacture mRNA that may affect the potency and safety of the mRNA vaccine in patients. Careful quantitation of dsRNA during manufacturing is critical to ensure that residual dsRNA is minimized in purified mRNA drug substances. In this work, we describe the development and implementation of a sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) to quantitate nanogram quantities of residual dsRNA contaminants in mRNA process intermediates using readily available commercial reagents. This sandwich ELISA developed in this study follows a standard protocol and can be easily adapted to most research laboratory environments. Additionally, a liquid handler coupled with an automated robotics system was utilized to increase assay throughput, improve precision, and reduce the analyst time requirement. The final automated sandwich ELISA was able to measure <10 ng/mL of dsRNA with a specificity for dsRNA over 2000-fold higher than mRNA, a variability of <15%, and a throughput of 72 samples per day.
Keywords: automation; dsRNA; high throughput; mRNA; sandwich ELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by the company Merck & Co., Inc. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and sensitive detection of dsRNA contaminants in in vitro-transcribed mRNA products.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Apr 8;32:445-453. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.04.005. eCollection 2023 Jun 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37181450 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on immune mechanism and control strategy of dsRNA impurities in mRNA vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2025 Dec;24(1):457-469. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2025.2510335. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 40401819 Review.
-
Double-stranded RNA reduction by chaotropic agents during in vitro transcription of messenger RNA.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Aug 4;29:618-624. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.08.001. eCollection 2022 Sep 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36090758 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Biolayer Interferometry (BLI)-Based Double-Stranded RNA Detection Method with Application in mRNA-Based Therapeutics and Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 19;16(9):1227. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091227. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339263 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of genome transcription in segmented dsRNA viruses.Adv Virus Res. 2000;55:185-229. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(00)55004-0. Adv Virus Res. 2000. PMID: 11050943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Size-exclusion chromatography with post-column nucleic acid staining and fluorescence detection for sensitive ribonucleic acid analysis.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Aug;417(20):4627-4636. doi: 10.1007/s00216-025-05979-w. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40586904 Free PMC article.
-
The design, manufacture and LNP formulation of mRNA for research use.Nat Protoc. 2025 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/s41596-025-01174-4. Online ahead of print. Nat Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40494942 Review.
References
-
- Miller J.B., Zhang S., Kos P., Xiong H., Zhou K., Perelman S.S., Zhu H., Siegwart D.J. Non-Viral CRISPR/Cas Gene Editing In Vitro and In Vivo Enabled by Synthetic Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017;56:1059–1063. doi: 10.1002/anie.201610209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bangel-Ruland N., Tomczak K., Fernández Fernández E., Leier G., Leciejewski B., Rudolph C., Rosenecker J., Weber W.-M. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-mRNA delivery: A novel alternative for cystic fibrosis gene therapy. J. Gene Med. 2013;15:414–426. doi: 10.1002/jgm.2748. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

