The Immunological and Epidemiological Effectiveness of Pediatric Single-Dose Vaccination against Hepatitis A 9 to 11 Years after Its Implementation in the Tyva Republic, the Russian Federation
- PMID: 39204032
- PMCID: PMC11359913
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12080907
The Immunological and Epidemiological Effectiveness of Pediatric Single-Dose Vaccination against Hepatitis A 9 to 11 Years after Its Implementation in the Tyva Republic, the Russian Federation
Abstract
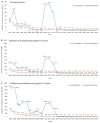
Since 2012, universal single-dose HAV vaccination in children aged 3 years and older has been implemented in the Tyva Republic, a region of the Russian Federation. The aim of this prospective non-interventional observational single-center study was to determine the immunological and epidemiological effectiveness of single-dose vaccination against hepatitis A 9 to 11 years after its implementation. The anti-HAV IgG antibodies were determined in two independent cohorts of children who were vaccinated with a single dose of monovalent pediatric inactivated vaccine (HAVRIX® 720 EU) in Tyva in 2012 and recruited 9 years (Year 9 Cohort) and 11 years (Year 11 Cohort) after immunization. The seroprotection rates defined as anti-HAV antibody concentrations ≥10 mIU/mL reached 99.4% (95% CI: 98.2-99.9% [501/504]) in the Year 9 Cohort, but decreased significantly to 75.4% (95% CI: 73.0-77.6% [1006/1335]) in the Year 11 Cohort (p < 0.0001). The anti-HAV geometric mean concentrations decreased from 1446.3 mIU/mL (95% CI: 1347.1-1545.4 mIU/mL) in the Year 9 Cohort to 282.6 mIU/mL (95% CI: 203.8-360.8, p < 0.0001) in the Year 11 Cohort. The HAV vaccination program resulted in zero rates of hepatitis A incidence in the Tyva Republic since 2016. However, the limited monitoring of HAV RNA in sewage and environmental samples demonstrated the ongoing circulation of both the regional epidemic strain of HAV genotype IA and another genotype IA strain imported recently from other parts of the Russian Federation, probably due to subclinical infections in non-vaccinated children under 3 years of age. Taken together, these data indicate the effectiveness of the single-dose HAV vaccination strategy but suggest the need to expand the vaccination program to include children aged 12 months and older to achieve maximum effectiveness.
Keywords: epidemiology; hepatitis A; hepatitis A vaccine; incidence; public health; single-dose vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funder was provided with the opportunity to review a preliminary version of this manuscript for factual accuracy, but has no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures

References
-
- Theeten H., Van Herck K., Van Der Meeren O., Crasta P., Van Damme P., Hens N. Long-term antibody persistence after vaccination with a 2-dose Havrix (inactivated hepatitis A vaccine): 20 years of observed data, and long-term model-based predictions. Vaccine. 2015;33:5723–5727. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.07.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

