Comparative Effectiveness of Various Multi-Antigen Vaccines in Controlling Campylobacter jejuni in Broiler Chickens
- PMID: 39204034
- PMCID: PMC11359598
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12080908
Comparative Effectiveness of Various Multi-Antigen Vaccines in Controlling Campylobacter jejuni in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
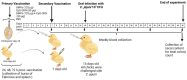
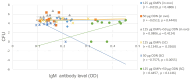
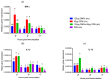
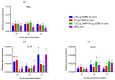
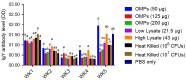
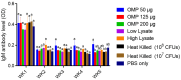
This study was undertaken to evaluate and compare the efficacy of different multi-antigen vaccines, including heat-inactivated, whole lysate, and subunit (outer membrane proteins [OMPs]) C. jejuni vaccines along with the immunostimulant CpG ODN in controlling Campylobacter colonization in chickens. In the first trial, 125 μg of C. jejuni OMPs and 50 μg of CpG ODN were administered individually or in combination, either in ovo to chick embryos or subcutaneously (SC) to one-day-old chicks. In the second trial, different concentrations of C. jejuni antigens (heat-killed, whole lysate, and OMPs) were administered SC to one-day-old chicks. The results of the first trial revealed that SC immunization with the combination of CpG ODN and C. jejuni OMPs elevated interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-13 gene expression in the spleen, significantly increased serum IgM and IgY antibody levels, and reduced cecal C. jejuni counts by approximately 1.2 log10. In contrast, in ovo immunization did not elicit immune responses or confer protection against Campylobacter. The results of the second trial showed that SC immunization with C. jejuni whole lysate or 200 μg OMPs reduced C. jejuni counts by approximately 1.4 and 1.1 log10, respectively. In conclusion, C. jejuni lysate and OMPs are promising vaccine antigens for reducing Campylobacter colonization in chickens.
Keywords: Campylobacter; CpG ODN; chickens; in ovo; outer membrane protein; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Campylobacter (Campylobacteriosis) [(accessed on 14 April 2024)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/index.html.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

