Comparative Immunogenicity of a High-Dose Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Vaccine with Rapid Immunization vs. Standard Schedule in HBV Vaccine-Naïve Adults Aged 25-55 in China
- PMID: 39204046
- PMCID: PMC11359784
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12080923
Comparative Immunogenicity of a High-Dose Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Vaccine with Rapid Immunization vs. Standard Schedule in HBV Vaccine-Naïve Adults Aged 25-55 in China
Abstract
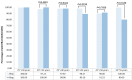
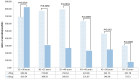
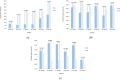
The 20 μg (0-1-6 month) hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccination is widely recommended for HBV vaccine-naïve immune adults in China. However, suboptimal protective responses may occur due to dose-series incompletion. We aim to investigate the immunogenicity of a 60 μg HB vaccine with a 0-2 month series among HBV vaccine-naïve immune adults aged 25-55 to assess potential alternative approaches for HB immunization. A two-center randomized controlled trial was carried out. Participants were randomly allocated to either the 20 μg (0-1-6 month) or the 60 μg (0-2 month) regimen. Blood samples were collected eight weeks after the final injection to measure the antibodies. A total of 583 adults (289 in the 20 μg regimen and 294 in the 60 μg regimen) were included. The seroprotection rates (SPRs) were 97.23% and 93.54% in the 20 μg and 60 μg regimens, respectively (p = 0.0261), and the geometric mean concentrations were 600.76 mIU/mL and 265.68 mIU/mL, respectively (p < 0.0001). The immunogenicity of the 60 μg regimen decreased significantly with age, particularly in adults aged 40 and older. The 60 μg regimen may be beneficial for adults under 40, especially those with poor compliance or in urgent need of immunization.
Keywords: adults; hepatitis B vaccine; high dosage; immunization; two-dose vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Global Hepatitis Report. 2017. [(accessed on 27 November 2023)]. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/publications/global-hepatitis-report-2017.
-
- Zhou Y.H., Wu C., Zhuang H. Vaccination against hepatitis B: The Chinese experience. Chin. Med. J. 2009;122:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Cui F.Q. Technical guide for adult hepatitis B immunization in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2011;32:1199–1203. (In Chinese) - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

