Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccination against Severe Symptoms and Death Among Geriatric Inpatients: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Macao
- PMID: 39204056
- PMCID: PMC11359226
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12080933
Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccination against Severe Symptoms and Death Among Geriatric Inpatients: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Macao
Abstract
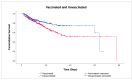
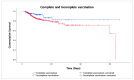
Monitoring the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination is critical for understanding if the vaccinated population, especially the elderly, is adequately protected from the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. This study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 vaccination on the severity of symptoms and mortality in hospitalized geriatric patients during the Omicron BF.7 surge in Macao. Data from electronic health records and vaccination registry of inpatients aged 60 years or above admitted to Kiang Wu Hospital from 12 December 2022 to 12 March 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. The study involved 848 people, including 426 vaccinated and 422 unvaccinated individuals. The mean CXR scores (8.95 ± 9.49 vs. 11.41 ± 10.81, p < 0.001) and the mean MEWS scores (0.96 ± 2.01 vs. 1.49 ± 2.45, p < 0.001) were lower in the vaccinated group. By comparing the dose counts, no significant difference was seen in the odds of death. Based on the time of the last vaccination, 128 people were categorized as complete and 298 as incomplete vaccination. The complete vaccination group showed a 54% (95% CI 0.23-0.91) reduction in mortality risk (p = 0.026). The study findings not only reconfirm the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination but, more importantly, highlight the importance of vaccination timing to maximize vaccines' protective effect.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccines; Omicron BF.7; SARS-CoV-2 variants; elderly; geriatrics; mortality; vaccination timing; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO COVID-19 Dashboard—Number of COVID-19 Deaths Reported to WHO (Cumulative Total) [(accessed on 20 July 2024)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c.
-
- World Health Organization The Different Types of COVID-19 Vaccines. [(accessed on 20 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-race-for-a-covi....
-
- The Food and Drug Administration FDA Approves First COVID-19 Vaccine. [(accessed on 20 July 2024)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-c....
-
- Tartof S.Y., Slezak J.M., Fischer H., Hong V., Ackerson B.K., Ranasinghe O.N., Frankland T.B., Ogun O.A., Zamparo J.M., Gray S., et al. Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2021;398:1407–1416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)02183-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous