Therapeutic Efficacy of Helianthemum lippii Extract and Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from the Extract against Cadmium-Induced Renal Nephrotoxicity in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 39204087
- PMCID: PMC11357364
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17080982
Therapeutic Efficacy of Helianthemum lippii Extract and Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from the Extract against Cadmium-Induced Renal Nephrotoxicity in Wistar Rats
Abstract
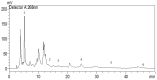
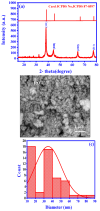
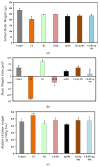
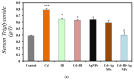
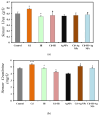
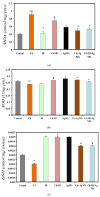
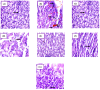
This study explored the therapeutic efficacy of Helianthemum lippii and silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) synthesized using a H. lippii extract to alleviate cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats. Sub-acute toxicity assessments of H. lippii (100 mg/kg, 1000 mg/kg, and 4000 mg/kg) and Ag NPs (2 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg) did not find any significant difference, compared with untreated control rats (n = 3 animals/group). Then, the adult Wistar rats were divided into one control (untreated/unexposed) and six experimental groups (n = 5/group): Ag NPs alone, H. lippii alone, exposure to 50 mg/kg CdCl2 in drinking water for 35 days, exposure to CdCl2 for 35 days followed by treatment with 0.1 mg/kg/day Ag NPs (intraperitoneal injection) and/or 100 mg/kg/day H. lippii by gavage for 15 days. In the CdCl2-exposed group, body weight decreased; urea, creatinine, and uric acid concentrations increased (p < 0.05 vs. control), indicative of nephrotoxicity, antioxidant defenses (SOD, GSH, and CAT) were reduced, and malondialdehyde concentration increased. Moreover, the kidney's architecture in CdCl2-exposed rats was altered: fibrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, glomerular destruction, and tubular dilatation. Treatment with H. lippii and/or Ag NPs after CdCl2 exposure improved some of the renal function and architecture alterations induced by CdCl2, and also increased body weight. This study underscores the potential therapeutic applications of H. lippii and Ag NPs to decrease oxidative stress and promote xenobiotic detoxification, in line with the growing emphasis on environmentally conscious practices in scientific research and healthcare.
Keywords: Helianthemum lippii; Wistar rats; biochemical parameters; cadmium toxicity; gavage; histopathology; intraperitoneal injection; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers at the time of submission.
Figures



References
-
- Monsefi M., Fereydouni B. The effects of cadmium pollution on female rat reproductive system. J. Infertil. Reprod. Biol. 2013;1:1–6. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2821-5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

