Roles of Sirtuins in Hearing Protection
- PMID: 39204103
- PMCID: PMC11357115
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17080998
Roles of Sirtuins in Hearing Protection
Abstract
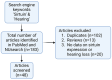
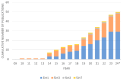
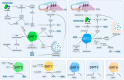
Hearing loss is a health crisis that affects more than 60 million Americans. Currently, sodium thiosulfate is the only drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to counter hearing loss. Sirtuins were proposed as therapeutic targets in the search for new compounds or drugs to prevent or cure age-, noise-, or drug-induced hearing loss. Sirtuins are proteins involved in metabolic regulation with the potential to ameliorate sensorineural hearing loss. The mammalian sirtuin family includes seven members, SIRT1-7. This paper is a literature review on the sirtuins and their protective roles in sensorineural hearing loss. Literature search on the NCBI PubMed database and NUsearch included the keywords 'sirtuin' and 'hearing'. Studies on sirtuins without relevance to hearing and studies on hearing without relevance to sirtuins were excluded. Only primary research articles with data on sirtuin expression and physiologic auditory tests were considered. The literature review identified 183 records on sirtuins and hearing. After removing duplicates, eighty-one records remained. After screening for eligibility criteria, there were forty-eight primary research articles with statistically significant data relevant to sirtuins and hearing. Overall, SIRT1 (n = 29) was the most studied sirtuin paralog. Over the last two decades, research on sirtuins and hearing has largely focused on age-, noise-, and drug-induced hearing loss. Past and current studies highlight the role of sirtuins as a mediator of redox homeostasis. However, more studies need to be conducted on the involvement of SIRT2 and SIRT4-7 in hearing protection.
Keywords: age-related hearing loss; antioxidant; apoptosis; cochlea; drug-induced hearing loss; noise-induced hearing loss; ototoxicity; outer hair cell; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sirtuins in gamete biology and reproductive physiology: emerging roles and therapeutic potential in female and male infertility.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 May 1;24(3):267-289. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy003. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 29447380 Review.
-
Drug-induced hearing loss: Listening to the latest advances.Therapie. 2024 Mar-Apr;79(2):283-295. doi: 10.1016/j.therap.2023.10.011. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Therapie. 2024. PMID: 37957052 Review.
-
Current understanding and future perspectives of the roles of sirtuins in the reprogramming and differentiation of pluripotent stem cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Mar;243(6):563-575. doi: 10.1177/1535370218759636. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29557214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Paradigm Shift in the Management of Atherosclerosis: Protective Role of Sirtuins in Atherosclerosis.Cureus. 2021 Jan 16;13(1):e12735. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12735. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33614337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional oriental medicine for sensorineural hearing loss: Can ethnopharmacology contribute to potential drug discovery?J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 1;231:409-428. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30439402 Review.
Cited by
-
N 1-methylnicotinamide promotes age-related cochlear damage via the overexpression of SIRT1.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Jan 31;19:1542164. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1542164. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39959464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cantó C., Houtkooper R.H., Pirinen E., Youn D.Y., Oosterveer M.H., Cen Y., Fernandez-Marcos P.J., Yamamoto H., Andreux P.A., Cettour-Rose P., et al. The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab. 2012;15:838–847. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

