Advances in Engineering Circular RNA Vaccines
- PMID: 39204292
- PMCID: PMC11356823
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13080692
Advances in Engineering Circular RNA Vaccines
Abstract
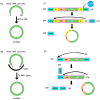
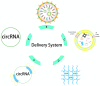
Engineered circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of single-stranded RNAs with head-to-tail covalently linked structures that integrate open reading frames (ORFs) and internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) with the function of coding and expressing proteins. Compared to mRNA vaccines, circRNA vaccines offer a more improved method that is safe, stable, and simple to manufacture. With the rapid revelation of the biological functions of circRNA and the success of Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus Type II (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccines, biopharmaceutical companies and researchers around the globe are attempting to develop more stable circRNA vaccines for illness prevention and treatment. Nevertheless, research on circRNA vaccines is still in its infancy, and more work and assessment are needed for their synthesis, delivery, and use. In this review, based on the current understanding of the molecular biological properties and immunotherapeutic mechanisms of circRNA, we summarize the current preparation methods of circRNA vaccines, including design, synthesis, purification, and identification. We discuss their delivery strategies and summarize the challenges facing the clinical application of circRNAs to provide references for circRNA vaccine-related research.
Keywords: RNA delivery; RNA therapeutics; circular RNA vaccines; circularization; mRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

