Novel Anti-Cancer Stem Cell Compounds: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39204369
- PMCID: PMC11360402
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081024
Novel Anti-Cancer Stem Cell Compounds: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
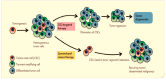
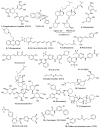
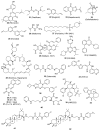
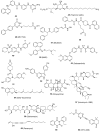
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) possess a significant ability to renew themselves, which gives them a strong capacity to form tumors and expand to encompass additional body areas. In addition, they possess inherent resistance to chemotherapy and radiation therapies used to treat many forms of cancer. Scientists have focused on investigating the signaling pathways that are highly linked to the ability of CSCs to renew themselves and maintain their stem cell properties. The pathways encompassed are Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, hedgehog, STAT3, NF-κB, PI-3K/Akt/mTOR, sirtuin, ALDH, MDM2, and ROS. Recent studies indicate that directing efforts towards CSC cells is essential in eradicating the overall cancer cell population and reducing the likelihood of tumor metastasis. As our comprehension of the mechanisms that stimulate CSC activity, growth, and resistance to chemotherapy advances, the discovery of therapeutic drugs specifically targeting CSCs, such as small-molecule compounds, holds the potential to revolutionize cancer therapy. This review article examines and analyzes the novel anti-CSC compounds that have demonstrated effective and selective targeting of pathways associated with the renewal and stemness of CSCs. We also discussed their special drug metabolism and absorption mechanisms. CSCs have been the subject of much study in cancer biology. As a possible treatment for malignancies, small-molecule drugs that target CSCs are gaining more and more attention. This article provides a comprehensive review of the current state of key small-molecule compounds, summarizes their recent developments, and anticipates the future discovery of even more potent and targeted compounds, opening up new avenues for cancer treatment.
Keywords: ALDH; Notch; Wnt/β-catenin; compound; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any financial affiliations with organizations or entities that have a financial stake in the subject matter or materials covered in the work. The authors have stated that there are no conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Therapeutic and Prognostic Relevance of Cancer Stem Cell Populations in Endometrial Cancer: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 25;15(15):1872. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151872. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the Molecular Signaling: Deciphering Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal Pathways.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2025 Jul 1;14(2):735-776. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.14.2.753. eCollection 2025. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2025. PMID: 40765762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials targeting cancer stem cells to overcome drug resistance and tumor recurrence.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 6;15:1499283. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1499283. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40548119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of p66Shc in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(14):e70737. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70737. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40690563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Trials of Cancer Stem Cells Targeted by Metal-Based Coordination Complexes: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 18;17(7):931. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070931. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

