Impact of Hot-Melt Extrusion on Glibenclamide's Physical and Chemical States and Dissolution Behavior: Case Studies with Three Polymer Blend Matrices
- PMID: 39204416
- PMCID: PMC11360095
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081071
Impact of Hot-Melt Extrusion on Glibenclamide's Physical and Chemical States and Dissolution Behavior: Case Studies with Three Polymer Blend Matrices
Abstract
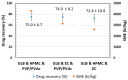
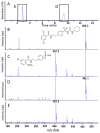
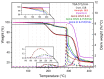
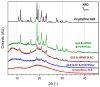
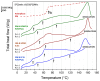
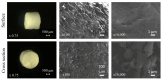
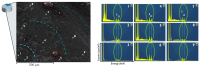
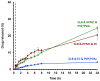
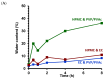
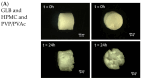
This research work dives into the complexity of hot-melt extrusion (HME) and its influence on drug stability, focusing on solid dispersions containing 30% of glibenclamide and three 50:50 polymer blends. The polymers used in the study are Ethocel Standard 10 Premium, Kollidon SR and Affinisol HPMC HME 4M. Glibenclamide solid dispersions are characterized using thermal analyses (thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry), X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. This study reveals the transformation of glibenclamide into impurity A during the HME process using mass spectrometry and TGA. Thus, it enables the quantification of the extent of degradation. Furthermore, this work shows how polymer-polymer blend matrices exert an impact on process parameters, the active pharmaceutical ingredient's physical state, and drug release behavior. In vitro dissolution studies show that the polymeric matrices investigated provide extended drug release (over 24 h), mainly dictated by the polymer's chemical nature. This paper highlights how glibenclamide is degraded during HME and how polymer selection crucially affects the sustained release dynamics.
Keywords: degradation; glibenclamide; hot-melt extrusion; solid dispersion; sustained drug release; ternary blends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Choiri S., Sulaiman T.N.S., Rohman A. Characterization of Eudragit types and Kollidon SR inter-polymer complexes and their effects on the drug release. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019;9:58–68. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2019.90708. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

