Enhancement of Antimicrobial Function by L/D-Lysine Substitution on a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide, Phylloseptin-TO2: A Structure-Related Activity Research Study
- PMID: 39204443
- PMCID: PMC11360180
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081098
Enhancement of Antimicrobial Function by L/D-Lysine Substitution on a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide, Phylloseptin-TO2: A Structure-Related Activity Research Study
Abstract
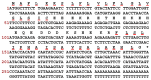
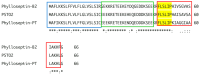
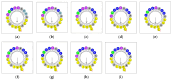
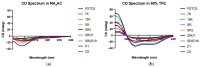
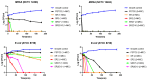
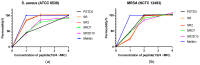
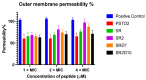
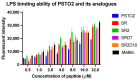
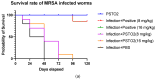
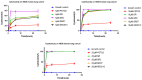
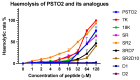
Antibiotic resistance poses a serious threat to public health globally, reducing the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics in treating bacterial infections. ESKAPE pathogens are a group of highly transmissible bacteria that mainly contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance and cause significant morbidity and mortality in humans. Phylloseptins, a class of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from Phyllomedusidae frogs, have been proven to have antimicrobial activity via membrane interaction. However, their relatively high cytotoxicity and low stability limit the clinical development of these AMPs. This project aims to study the antimicrobial activity and mechanisms of a phylloseptin-like peptide, phylloseptin-TO2 (PSTO2), following rational amino acid modification. Here, PSTO2 (FLSLIPHAISAVSALAKHL-NH2), identified from the skin secretion of Phyllomedusa tomopterna, was used as the template for modification to enhance antimicrobial activity. Adding positive charges to PSTO2 through substitution with L-lysines enhanced the interaction of the peptides with cell membranes and improved their antimicrobial efficacy. The analogues SRD7 and SR2D10, which incorporated D-lysines, demonstrated significant antimicrobial effects against Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) while also showing reduced haemolytic activity and cytotoxicity, resulting in a higher therapeutic index. Additionally, SRD7, modified with D-lysines, exhibited notable anti-proliferative properties against human lung cancer cell lines, including H838 and H460. This study thus provides a potential development model for new antibacterial and anti-cancer drugs combating antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: D-lysine substitution; anti-cancer activity; antimicrobial peptide; membrane interaction; phylloseptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterisation of the Antimicrobial Peptide, Phylloseptin-PT, from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa tarsius, and Comparison of Activity with Designed, Cationicity-Enhanced Analogues and Diastereomers.Molecules. 2016 Dec 3;21(12):1667. doi: 10.3390/molecules21121667. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27918477 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Phylloseptins that Defense against Gram-Positive Bacteria and Inhibit the Proliferation of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line, from the Skin Secretions of Phyllomedusa Frogs.Molecules. 2017 Aug 29;22(9):1428. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091428. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28850103 Free PMC article.
-
Phylloseptin-PBa--A Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide from the Skin Secretion of the Peruvian Purple-Sided Leaf Frog (Phyllomedusa Baltea) Which Exhibits Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Dec 1;7(12):5182-93. doi: 10.3390/toxins7124878. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26633506 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the development of antimicrobial peptides against ESKAPE pathogens.Heliyon. 2024 May 24;10(11):e31958. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31958. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38868046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: From Design to Clinical Application.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Mar 6;11(3):349. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11030349. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering of antimicrobial peptide Brevinin-1pl: arginine, lysine, and histidine substitutions enhance antimicrobial-anticancer efficacy with reduced cytotoxicity.Front Chem. 2025 May 19;13:1579097. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1579097. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40458657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pancu D.F., Scurtu A., Macasoi I.G., Marti D., Mioc M., Soica C., Coricovac D., Horhat D., Poenaru M., Dehelean C. Antibiotics: Conventional Therapy and Natural Compounds with Antibacterial Activity—A Pharmaco-Toxicological Screening. Antibiotics. 2021;10:401. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10040401. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

