Surface Treatment of Additively Manufactured Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) by Centrifugal Disc Finishing Process: Identification of the Key Parameters
- PMID: 39204568
- PMCID: PMC11359199
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16162348
Surface Treatment of Additively Manufactured Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) by Centrifugal Disc Finishing Process: Identification of the Key Parameters
Abstract
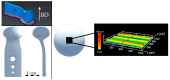
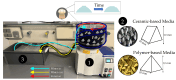
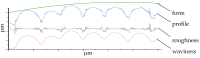
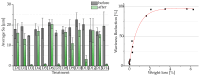
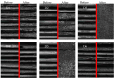
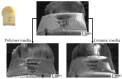
Polyetheretherketone is a promising material for implants due to its good mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility. Its accessibility to a wide range of applications is facilitated by the ability to process it with an easy-to-use manufacturing process such as fused filament fabrication. The elimination of disadvantages associated with the manufacturing process, such as a poor surface quality, is a main challenge to deal with. As part of the mass finishing process, centrifugal disc finishing has demonstrated good results in surface optimization, making it a promising candidate for the post-processing of additively manufactured parts. The objective of this study is to identify the key parameters of the centrifugal disc finishing process on the waviness of additively manufactured PEEK specimens, which has not been investigated previously. The waviness of the specimen was investigated by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), while weight loss was additionally tracked. Six parameters were investigated: type, amount and speed of media, use of compound, amount of water and time. Type of media, time and speed were found to significantly influence waviness reduction and weight loss. Surface electron microscopy images demonstrated the additional effects of deburring and corner rounding. Results on previous studies with specimens made of metal showed similar results. Further investigation is required to optimize waviness reduction and polish parts in a second post-processing step.
Keywords: 3D printing; PEEK; additive manufacturing; centrifugal disc finishing; fused deposition modeling; fused filament fabrication; high-performance polymers; mass finishing; post-processing of 3D printed parts; surface treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Verma S., Sharma N., Kango S., Sharma S. Developments of PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) as a biomedical material: A focused review. Eur. Polym. J. 2021;147:110295. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110295. - DOI
-
- Siewert B., Plaza-Castro M., Sereno N., Jarman-Smith M. PEEK Biomaterials Handbook. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Applications of PEEK in the Dental Field; pp. 333–342. - DOI
-
- Haleem A., Javaid M. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and its 3D printed implants applications in medical field: An overview. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health. 2019;7:571–577. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2019.01.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

