Complex Residual Attention U-Net for Fast Ultrasound Imaging from a Single Plane-Wave Equivalent to Diverging Wave Imaging
- PMID: 39204807
- PMCID: PMC11360587
- DOI: 10.3390/s24165111
Complex Residual Attention U-Net for Fast Ultrasound Imaging from a Single Plane-Wave Equivalent to Diverging Wave Imaging
Abstract
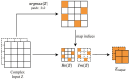
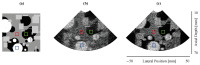
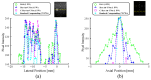
Plane wave imaging persists as a focal point of research due to its high frame rate and low complexity. However, in spite of these advantages, its performance can be compromised by several factors such as noise, speckle, and artifacts that affect the image quality and resolution. In this paper, we propose an attention-based complex convolutional residual U-Net to reconstruct improved in-phase/quadrature complex data from a single insonification acquisition that matches diverging wave imaging. Our approach introduces an attention mechanism to the complex domain in conjunction with complex convolution to incorporate phase information and improve the image quality matching images obtained using coherent compounding imaging. To validate the effectiveness of this method, we trained our network on a simulated phased array dataset and evaluated it using in vitro and in vivo data. The experimental results show that our approach improved the ultrasound image quality by focusing the network's attention on critical aspects of the complex data to identify and separate different regions of interest from background noise.
Keywords: complex convolutional neural networks; deep learning; image reconstruction; in-phase/quadrature signal; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Trees H. Optimum Array Processing—Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2002.
-
- Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Hinton G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In: Pereira F., Burges C., Bottou L., Weinberger K., editors. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Volume 25 Curran Associates, Inc.; Red Hook, NY, USA: 2012.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

