Sea Horse Optimization-Deep Neural Network: A Medication Adherence Monitoring System Based on Hand Gesture Recognition
- PMID: 39204920
- PMCID: PMC11360803
- DOI: 10.3390/s24165224
Sea Horse Optimization-Deep Neural Network: A Medication Adherence Monitoring System Based on Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract
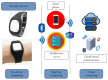
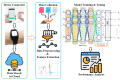
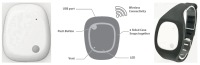
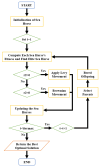
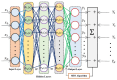
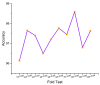
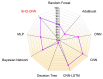
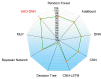
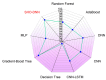
Medication adherence is an essential aspect of healthcare for patients and is important for achieving medical objectives. However, the lack of standard techniques for measuring adherence is a global concern, making it challenging to accurately monitor and measure patient medication regimens. The use of sensor technology for medication adherence monitoring has received much attention lately since it makes it possible to continuously observe patients' medication adherence behavior. Sensor devices or smart wearables utilize state-of-the-art machine learning (ML) methods to analyze intricate data patterns and provide predictions accurately. The key aim of this work is to develop a sensor-based hand gesture recognition model to predict medication activities. In this research, a smart sensor device-based hand gesture prediction model is developed to recognize medication intake activities. The device includes a tri-axial gyroscope, geometric, and accelerometer sensors to sense and gather data from hand gestures. A smartphone application gathers hand gesture data from the sensor device, which is then stored in the cloud database in a .csv format. These data are collected, processed, and classified to recognize the medication intake activity using the proposed novel neural network model called Sea Horse Optimization-Deep Neural Network (SHO-DNN). The SHO technique is implemented to update the biases and weights and the number of hidden layers in the DNN model. By updating these parameters, the DNN model is improved in classifying the samples of hand gestures to identify the medication activities. The research model demonstrates impressive performance, with an accuracy of 98.59%, sensitivity of 97.82%, precision of 98.69%, and an F1 score of 98.48%. Hence, the proposed model outperformed the most available models in all the aforementioned aspects. The results indicate that this model is a promising approach for medication adherence monitoring in healthcare applications, instilling confidence in its effectiveness.
Keywords: hand gestures; machine learning; medication adherence; sensor; smart wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

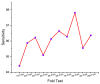
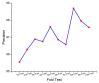
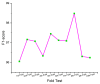
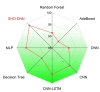
References
-
- Paulsamy P., Ashraf R., Alshahrani S.H., Periannan K., Qureshi A.A., Venkatesan K., Manoharan V., Govindasamy N., Prabahar K., Arumugam T., et al. Social Support, Self-Care Behaviour and Self-Efficacy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare. 2021;9:1607. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9111607. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

