Impact of Measurement Uncertainty on Fault Diagnosis Systems: A Case Study on Electrical Faults in Induction Motors
- PMID: 39204958
- PMCID: PMC11360190
- DOI: 10.3390/s24165263
Impact of Measurement Uncertainty on Fault Diagnosis Systems: A Case Study on Electrical Faults in Induction Motors
Abstract
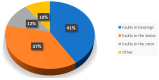
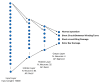
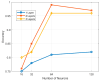
Classification systems based on machine learning (ML) models, critical in predictive maintenance and fault diagnosis, are subject to an error rate that can pose significant risks, such as unnecessary downtime due to false alarms. Propagating the uncertainty of input data through the model can define confidence bands to determine whether an input is classifiable, preferring to indicate a result of unclassifiability rather than misclassification. This study presents an electrical fault diagnosis system on asynchronous motors using an artificial neural network (ANN) model trained with vibration measurements. It is shown how vibration analysis can be effectively employed to detect and locate motor malfunctions, helping reduce downtime, improve process control and lower maintenance costs. In addition, measurement uncertainty information is introduced to increase the reliability of the diagnosis system, ensuring more accurate and preventive decisions.
Keywords: anomaly detection; artificial neural networks (ANNs); fault diagnosis; induction motors; measurement uncertainty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Henao H., Capolino G.-A., Fernandez-Cabanas M., Filippetti F., Bruzzese C., Strangas E., Pusca R., Estima J., Riera-Guasp M., Hedayati-Kia S. Trends in fault diagnosis for electrical machines: A review of diagnostic techniques. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2014;8:31–42. doi: 10.1109/MIE.2013.2287651. - DOI
-
- Thomson W.T. Online motor current signature analysis prevents premature failure of large induction motor drives operating in the North Sea oil and gas industry; Proceedings of the 9th European Fluid Machinery Congress Applying Latest Technology to New and Existing Process Equipment, Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Fluid Machinery Group; The Hague, The Netherlands. 23–26 April 2006; pp. 263–272.
-
- Thomson W.T., Fenger M. Industrial application of current signature analysis to diagnose faults in 3-phase squirrel cage induction motors; Proceedings of the IEEE Conference Record of Annual Pulp and Paper Industry Technical Conference; Atlanta, GA, USA. 19–23 June 2000; pp. 205–211.
-
- Samsi R., Ray A., Mayer J. Early detection of stator voltage imbalance in three-phase induction motors. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009;79:239–245. doi: 10.1016/j.epsr.2008.06.004. - DOI
-
- Wadhwani S., Gupta S.P., Kumar V. Fault classification for rolling element bearing in electric machines. IETE J. Res. 2008;54:264–275. doi: 10.4103/0377-2063.44230. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

