Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cancer Cells Using Antibody-Functionalized Paddle Screw-Type Devices and Detection of Exosomal miRNA Using Piezoelectric Biosensor
- PMID: 39205093
- PMCID: PMC11359151
- DOI: 10.3390/s24165399
Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cancer Cells Using Antibody-Functionalized Paddle Screw-Type Devices and Detection of Exosomal miRNA Using Piezoelectric Biosensor
Abstract
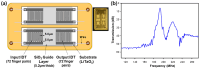
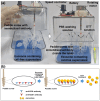
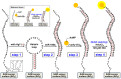
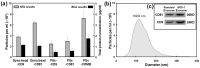
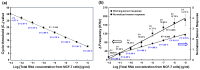
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles produced by almost all cell types in the human body, and exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that are known to serve as important biomarkers for diseases such as cancer. Given that the upregulation of miR-106b is closely associated with several types of malignancies, the sensitive and accurate detection of miR-106b is important but difficult. In this study, a surface acoustic wave (SAW) biosensor was developed to detect miR-106b isolated from cancer cells based on immunoaffinity separation technique using our unique paddle screw device. Our novel SAW biosensor could detect a miR-106b concentration as low as 0.0034 pM in a linear range from 0.1 pM to 1.0 μM with a correlation coefficient of 0.997. Additionally, we were able to successfully detect miR-106b in total RNA extracted from the exosomes isolated from the MCF-7 cancer cell line, a model system for human breast cancer, with performance comparable to commercial RT-qPCR methods. Therefore, the exosome isolation by the paddle screw method and the miRNA detection using the SAW biosensor has the potential to be used in basic biological research and clinical diagnosis as an alternative to RT-qPCR.
Keywords: MCF-7 cell line; exosome; immunoaffinity separation; microRNA; paddle screw; surface acoustic wave (SAW) biosensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In situ multiplex detection of serum exosomal microRNAs using an all-in-one biosensor for breast cancer diagnosis.Analyst. 2020 May 7;145(9):3289-3296. doi: 10.1039/d0an00393j. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Analyst. 2020. PMID: 32255115
-
A ratiometric fluorescent biosensor based on self-fluorescent MOF and target-triggered rolling circle amplification for sensitive detection of exosome-derived miRNA.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Aug 15;1221:340136. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340136. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35934407
-
A microfluidic-based chemiluminescence biosensor for sensitive multiplex detection of exosomal microRNAs based on hybridization chain reaction.Talanta. 2025 Jan 1;281:126838. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126838. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 39255623
-
Exosomal miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers: Challenges and opportunities.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):6370-6380. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26481. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29323722 Review.
-
Biosensor-based methods for exosome detection with applications to disease diagnosis.Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Jul 1;279:117362. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117362. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 40157151 Review.
Cited by
-
Piezoelectric Chemosensors and Biosensors in Medical Diagnostics.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;15(3):197. doi: 10.3390/bios15030197. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects and mechanisms of exosomes in microenvironment angiogenesis in breast cancer: An updated review.Oncol Res. 2025 May 29;33(6):1323-1334. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.059113. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40486870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

