Bearing Dynamics Modeling Based on the Virtual State-Space and Hammerstein-Wiener Model
- PMID: 39205105
- PMCID: PMC11359357
- DOI: 10.3390/s24165410
Bearing Dynamics Modeling Based on the Virtual State-Space and Hammerstein-Wiener Model
Abstract
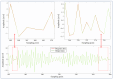
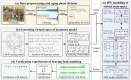
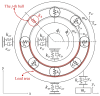
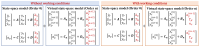
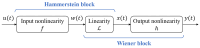
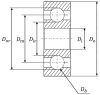
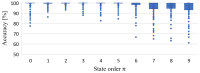
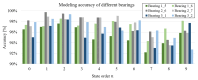
This study investigates a novel approach for assessing the health status of rotating machinery transmission systems by analyzing the dynamic degradation of bearings. The proposed method generates multi-dimensional data by creating virtual states and constructs a multi-dimensional model using virtual state-space in conjunction with mechanism model analysis. Innovatively, the Hammerstein-Wiener (HW) modeling technique from control theory is applied to identify these dynamic multi-dimensional models. The modeling experiments are performed, focusing on the model's input and output types, the selection of nonlinear module estimators, the configuration of linear module transfer functions, and condition transfer. Dynamic degradation response signals are generated, and the method is validated using four widely recognized databases consisting of accurate measurement signals collected by vibration sensors. Experimental results demonstrated that the model achieved a modeling accuracy of 99% for multiple bearings under various conditions. The effectiveness of this dynamic modeling method is further confirmed through comparative experimental data and signal images. This approach offers a novel reference for evaluating the health status of transmission systems.
Keywords: Hammerstein–Wiener; Prognostics and Health Management; bearing; data-driven; dynamic modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nonlinear predictive control for Hammerstein-Wiener systems.ISA Trans. 2015 Mar;55:49-62. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.09.018. Epub 2014 Oct 23. ISA Trans. 2015. PMID: 25451816
-
Flex Sensor Compensator via Hammerstein-Wiener Modeling Approach for Improved Dynamic Goniometry and Constrained Control of a Bionic Hand.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 10;19(18):3896. doi: 10.3390/s19183896. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31509987 Free PMC article.
-
State Space Formulation of Nonlinear Vibration Responses Collected from a Dynamic Rotor-Bearing System: An Extension of Bearing Diagnostics to Bearing Prognostics.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Feb 14;17(2):369. doi: 10.3390/s17020369. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28216586 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of nonlinear biological systems: Wiener and Hammerstein cascade models.Biol Cybern. 1986;55(2-3):135-44. doi: 10.1007/BF00341929. Biol Cybern. 1986. PMID: 3801534
-
Identification of a Modified Wiener-Hammerstein System and Its Application in Electrically Stimulated Paralyzed Skeletal Muscle Modeling.Automatica (Oxf). 2009 Mar;45(3):736-743. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.09.023. Automatica (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 23467426 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural Dynamics Analysis of a Large Aperture Space Telescope Based on the Linear State Space Method.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;25(8):2476. doi: 10.3390/s25082476. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40285166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rai A., Upadhyay S.H. A review on signal processing techniques utilized in the fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. Tribol. Int. 2016;96:289–306.
-
- Jalan A.K., Mohanty A. Model based fault diagnosis of a rotor–bearing system for misalignment and unbalance under steady-state condition. J. Sound Vib. 2009;327:604–622.
-
- Mishra C., Samantaray A., Chakraborty G. Ball bearing defect models: A study of simulated and experimental fault signatures. J. Sound Vib. 2017;400:86–112.
-
- Xi S., Cao H., Chen X., Niu L. Dynamic modeling of machine tool spindle bearing system and model based diagnosis of bearing fault caused by collision. Procedia CIRP. 2018;77:614–617.
-
- Javanmardi D., Rezvani M.A. Rail vehicle axlebox roller bearing life and failure analysis based on the Hertz contact theory, finite element modeling, and field observations. World J. Eng. 2023 doi: 10.1108/WJE-01-2023-0010. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

