Prevalence and Sequence Analysis of Equine Rhinitis Viruses among Horses in Poland
- PMID: 39205178
- PMCID: PMC11359465
- DOI: 10.3390/v16081204
Prevalence and Sequence Analysis of Equine Rhinitis Viruses among Horses in Poland
Abstract
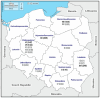
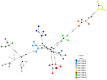
Equine rhinitis A (ERAV) and B (ERBV) viruses are respiratory pathogens with worldwide distribution. The current study aimed to determine the frequency of infection of ERAV and ERBV among horses and foals at Polish national studs, and to determine genetic variability within the viruses obtained. Virus-specific quantitative RT-PCR assays targeting a 5' untranslated region were used to screen nasal swabs collected from 621 horses at 16 national horse studs from throughout Poland, including 553 healthy horses and 68 horses with respiratory disease. A partial DNA polymerase gene was amplified and sequenced from the qRT-PCR-positive samples. The obtained sequences were analysed using phylogeny and genetic network analysis. None of the nasal swabs were positive for ERAV, whereas ERBV was found in 11/621 (1.78%) samples collected from 10 healthy horses and one foal affected by respiratory disease. Partial DNA polymerase gene sequence variability was correlated with individual horses and studs from which samples were collected when only Polish sequences were analysed, but there was no correlation between country of origin and ERBV sequence when Polish and international sequences were included in the network. The report presents the first detection of ERBV in Poland.
Keywords: ERAV; ERBV; equine rhinitis viruses; haplotype network; horses; sequence analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, ICTV Masters Species List 2022 MSL38 v3. [(accessed on 10 April 2024)]. Available online: https://ictv.global/msl.
-
- Dynon K., Black W.D., Ficorilli N., Hartley C.A., Studdert M.J. Detection of viruses in nasal swab samples from horses with acute, febrile, respiratory disease using virus isolation, polymerase chain reaction and serology. Aust. Vet. J. 2007;85:46–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.2006.00096.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

