Detection of Bombali Virus in a Mops condylurus Bat in Kyela, Tanzania
- PMID: 39205201
- PMCID: PMC11358901
- DOI: 10.3390/v16081227
Detection of Bombali Virus in a Mops condylurus Bat in Kyela, Tanzania
Abstract
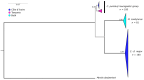
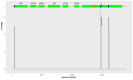
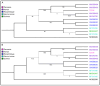
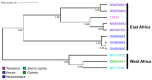
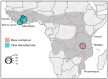
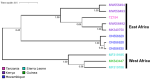
Bombali virus (BOMV) is a novel Orthoebolavirus that has been detected in free-tailed bats in Sierra Leone, Guinea, Kenya, and Mozambique. We screened our collection of 349 free-tailed bat lungs collected in Côte d'Ivoire and Tanzania for BOMV RNA and tested 228 bat blood samples for BOMV antibodies. We did not detect BOMV-specific antibodies but found BOMV RNA in a Mops condylurus bat from Tanzania, marking the first detection of an ebolavirus in this country. Our findings further expand the geographic range of BOMV and support M. condylurus' role as a natural BOMV host.
Keywords: Filoviridae; Orthoebolavirus bombaliense; ebolavirus; free-tailed bat; natural host.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Ebola Virus Disease. [(accessed on 21 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ebola-virus-disease.
-
- Kinganda-Lusamaki E., Whitmer S., Lokilo-Lofiko E., Amuri-Aziza A., Muyembe-Mawete F., Makangara-Cigolo J.C., Makaya G., Mbuyi F., Whitesell A., Kallay R., et al. 2020 Ebola virus disease outbreak in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo: A retrospective genomic characterisation. Lancet Microbe. 2024;5:e109–e118. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00259-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

