Update on Hepatitis C Vaccine: Results and Challenges
- PMID: 39205311
- PMCID: PMC11359353
- DOI: 10.3390/v16081337
Update on Hepatitis C Vaccine: Results and Challenges
Abstract
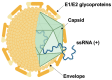
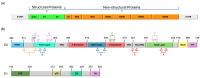
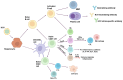
Therapy against the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) has significantly improved with the introduction of direct-acting antiviral drugs (DAAs), achieving over 95% sustained virological response (SVR). Despite this, the development of an effective anti-HCV vaccine remains a critical challenge due to the low number of patients treated with DAAs and the occurrence of HCV reinfections in high-risk groups. Current vaccine strategies aim to stimulate either B-cell or T-cell responses. Vaccines based on E1 and E2 proteins can elicit broad cross-neutralizing antibodies against all major HCV genotypes, though with varying efficiencies and without full protection against infection. In humans, the neutralizing antibodies induced by such vaccines mainly target the AR3 region, but their levels are generally insufficient for broad neutralization. Various HCV proteins expressed through different viral vectors have been utilized to elicit T cell immune responses, showing sustained expansion of HCV-specific effector memory T cells and improved proliferation and polyfunctionality of memory T cells over time. However, despite these advancements, the frequency and effectiveness of T-cell responses remain limited.
Keywords: hepatitis C; immune response; immunogenicity; neutralizing antibody; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blach S., Zeuzem S., Manns M., Altraif I., Duberg A.-S., Muljono D.H., Waked I., Alavian S.M., Lee M.-H., Negro F., et al. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;2:161–176. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30181-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Hepatitis Report 2017. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Ghiglione Y., Polo M.L., Urioste A., Rhodes A., Czernikier A., Trifone C., Quiroga M.F., Sisto A., Patterson P., Salomón H., et al. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Clearance After Treatment With Direct-Acting Antivirals in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-HCV Coinfection Modulates Systemic Immune Activation and HIV Transcription on Antiretroviral Therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020;7:ofaa115. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

