Advancing Equitable Ambulatory Telehealth Through Dashboard Development
- PMID: 39205676
- PMCID: PMC11347865
- DOI: 10.1089/tmr.2024.0033
Advancing Equitable Ambulatory Telehealth Through Dashboard Development
Abstract
Telehealth has the potential to improve access to health care by mitigating barriers related to geography, time, and finances. However, the increased adoption of ambulatory telehealth has inadvertently widened access gaps for socially disadvantaged and marginalized populations. Quality improvement approaches are a valuable strategy to address health care access inequities and disparities, involving data-driven implementation, assessment, and adaptation of tests of change over time. Because these iterative changes and interventions are data-driven, a critical element of quality improvement requires ongoing data collection and monitoring. This perspective describes the development and validation processes of a telehealth equity dashboard. This dashboard is currently available for use by our health system leaders, providers, and clinic staff. The overall objective of this dashboard is to identify and track inequities and to improve equitable ambulatory telehealth access across diverse patient groups. Lessons learned from creating this dashboard can inform other health care systems of how to develop and validate telehealth data feedback systems to promote quality improvement efforts to advance telehealth equity and accessibility.
Keywords: dashboard systems; digital health; health equity; quality improvement; telemedicine.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.
Figures
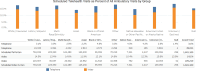
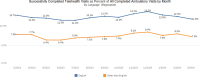
References
-
- Gelburd R. Examining the State of Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic. United Hospital Fund; 2021.
-
- Myers CR. Using telehealth to remediate rural mental health and healthcare disparities. Issues Ment Health Nurs 2019;40(3):233–239. - PubMed
-
- Anaya YBM, Mota AB, Hernandez GD, et al. Post-pandemic telehealth policy for primary care: An equity perspective. J Am Board Fam Med 2022;35(3):588–592. - PubMed
-
- Lyu M, Zhao Q, Yang Y, et al. Benefits of and barriers to telehealth for the informal caregivers of elderly individuals in rural areas: A scoping review. Aust J Rural Health 2022;30(4):442–457. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez JA, Saadi A, Schwamm LH, et al. Disparities in telehealth use among California patients with limited English proficiency: Study examines disparities in telehealth use among California patients with limited English proficiency. Health Aff (Millwood) 2021;40(3):487–495. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
