Effect of IVIG therapy on pregnant women with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39205682
- PMCID: PMC11349655
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1381461
Effect of IVIG therapy on pregnant women with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy on unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (URSA).
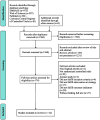
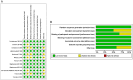
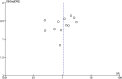
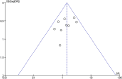
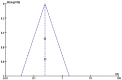
Methods: We retrieved all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) related to the effect of IVIG therapy on URSA in the following databases: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials before April 30, 2023, according to the PRISMA statement. The therapeutic effect of IVIG was measured by live birth rates. Quality assessment was conducted independently by two reviewers, based on the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. For the meta-analysis, we used odds ratios (random effects model and fixed effects model). The between-study heterogeneity was assessed by the Q test. Publication bias was assessed by funnel plots.
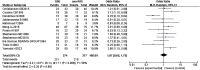
Results: A total of 12 studies with 751 participants were included in this meta-analysis. There was no statistical significance [OR = 1.07, 95%CI (0.65, 1.75), P=0.80] between the IVIG group and the non-IVIG group, including low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) plus low-dose aspirin (LDA), intralipid, multivitamins, albumin, and normal saline. A subgroup analysis was conducted according to the different treatment regimens of the non-IVIG group. Compared to the placebo group, including multivitamins, albumin, and saline, the live birth rate of the IVIG group is superior, but there was no statistical significance [OR =1.43, 95%CI (0.99, 2.07), P=0.05]. Another subgroup analysis was performed according to URSA with positive for antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs). Results showed the live birth rate of IVIG on URSA with positive for aPLs is inferior to that of LMWH plus LDA [OR = 0.25, 95%CI (0.11, 0.55), P=0.0007].
Conclusions: IVIG didn't increase the live birth rate of URSA compared to placebo. Conversely, compared with the IVIG, the LMWH plus LDA treatment schedule can increase the live birth rate of URSA with positive for aPLs.
Keywords: antiphospholipid syndrome; intravenous immunoglobulin; meta-analysis; treatment; unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion.
Copyright © 2024 Ling, Xu, Tian, Chen, Mo and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

