CYP2D6 copy number determination using digital PCR
- PMID: 39206265
- PMCID: PMC11349684
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1429286
CYP2D6 copy number determination using digital PCR
Abstract
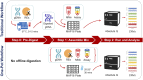
Background: CYP2D6 testing is increasingly used to guide drug therapy and thus, reliable methods are needed to test this complex and polymorphic gene locus. A particular challenge arises from the detection and interpretation of structural variants (SVs) including gene deletions, duplications, and hybrids with the CYP2D7 pseudogene. This study validated the Absolute Q™ platform for digital PCR-based CYP2D6 copy number variation (CNV) determination by comparing results to those obtained with a previously established method using the QX200 platform. In addition, protocols for streamlining CYP2D6 CNV testing were established and validated including the "One-pot" single-step restriction enzyme digestion and a multiplex assay simultaneously targeting the CYP2D6 5'UTR, intron 6, and exon 9 regions.
Methods: Genomic DNA (gDNA) samples from Coriell (n = 13) and from blood, saliva, and liver tissue (n = 17) representing 0-6 copies were tested on the Absolute Q and QX200 platforms. Custom TaqMan™ copy number (CN) assays targeting CYP2D6 the 5'UTR, intron 6, and exon 9 regions and a reference gene assay (TERT or RNaseP) were combined for multiplexing by optical channel. In addition, two digestion methods (One-pot digestion and traditional) were assessed. Inconclusive CN values on the Absolute Q were resolved using an alternate reference gene and/or diluting gDNA.
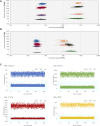
Results: Overall, results between the two platforms and digestions methods were consistent. The "One-pot" digestion method and optically multiplexing up to three CYP2D6 regions yielded consistent result across DNA sample types and diverse SVs, reliably detecting up to 6 gene copies. Rare variation in reference genes were found to interfere with results and interpretation, which were resolved by using a different reference.
Conclusion: The Absolute Q produced accurate and reliable CYP2D6 copy number results allowing for a streamlined and economical protocol using One-pot digestion and multiplexing three target regions. Protocols are currently being expanded to other pharmacogenes presenting with SVs/CNVs.
Keywords: Absolute Q; CYP2D6; One-pot; copy number variation; digital PCR; multiplex; quantitative PCR; reference gene.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Lin, Boone, Stevens and Gaedigk.
Conflict of interest statement
Thermo Fisher Scientific (TFS) provided the Applied Biosystems QuantStudio Absolute Q Digital PCR System and copy number assays. LL and JS are employees of TFS. The author AG declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bell G. C., Caudle K. E., Whirl-Carrillo M., Gordon R. J., Hikino K., Prows C. A., et al. (2017). Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6 genotype and use of ondansetron and tropisetron. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 102, 213–218. 10.1002/cpt.598 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bousman C. A., Stevenson J. M., Ramsey L. B., Sangkuhl K., Hicks J. K., Strawn J. R., et al. (2023). Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A genotypes and serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 114, 51–68. 10.1002/cpt.2903 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

