Unveiling Molecular Diversity in Cerebral Thrombi via Spatial Transcriptomics
- PMID: 39206540
- PMCID: PMC11421970
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.047907
Unveiling Molecular Diversity in Cerebral Thrombi via Spatial Transcriptomics
Keywords: atherosclerosis; middle cerebral artery; stroke; thrombectomy; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
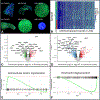
References
-
- Bergholtz H, Carter JM, Cesano A, Cheang MCU, Church SE, Divakar P, Fuhrman CA, Goel S, Gong J, Guerriero JL, et al. Best Practices for Spatial Profiling for Breast Cancer Research with the GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler. Cancers [Internet]. 2021;13. Available from: 10.3390/cancers13174456 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

