Whole Cell Luminescence-Based Screen for Inhibitors of the Bacterial Sec Machinery
- PMID: 39207823
- PMCID: PMC11411707
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00264
Whole Cell Luminescence-Based Screen for Inhibitors of the Bacterial Sec Machinery
Abstract
There is a pressing need for new antibiotics to combat rising resistance to those already in use. The bacterial general secretion (Sec) system has long been considered a good target for novel antimicrobials thanks to its irreplacable role in maintaining cell envelope integrity, yet the lack of a robust, high-throughput method to screen for Sec inhibition has so far hampered efforts to realize this potential. Here, we have adapted our recently developed in vitro assay for Sec activity─based on the split NanoLuc luciferase─to work at scale and in living cells. A simple counterscreen allows compounds that specifically target Sec to be distinguished from those with other effects on cellular function. As proof of principle, we have applied this assay to a library of 5000 compounds and identified a handful of moderately effective in vivo inhibitors of Sec. Although these hits are unlikely to be potent enough to use as a basis for drug development, they demonstrate the efficacy of the screen. We therefore anticipate that the methods presented here will be scalable to larger compound libraries, in the ultimate quest for Sec inhibitors with clinically relevant properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
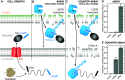


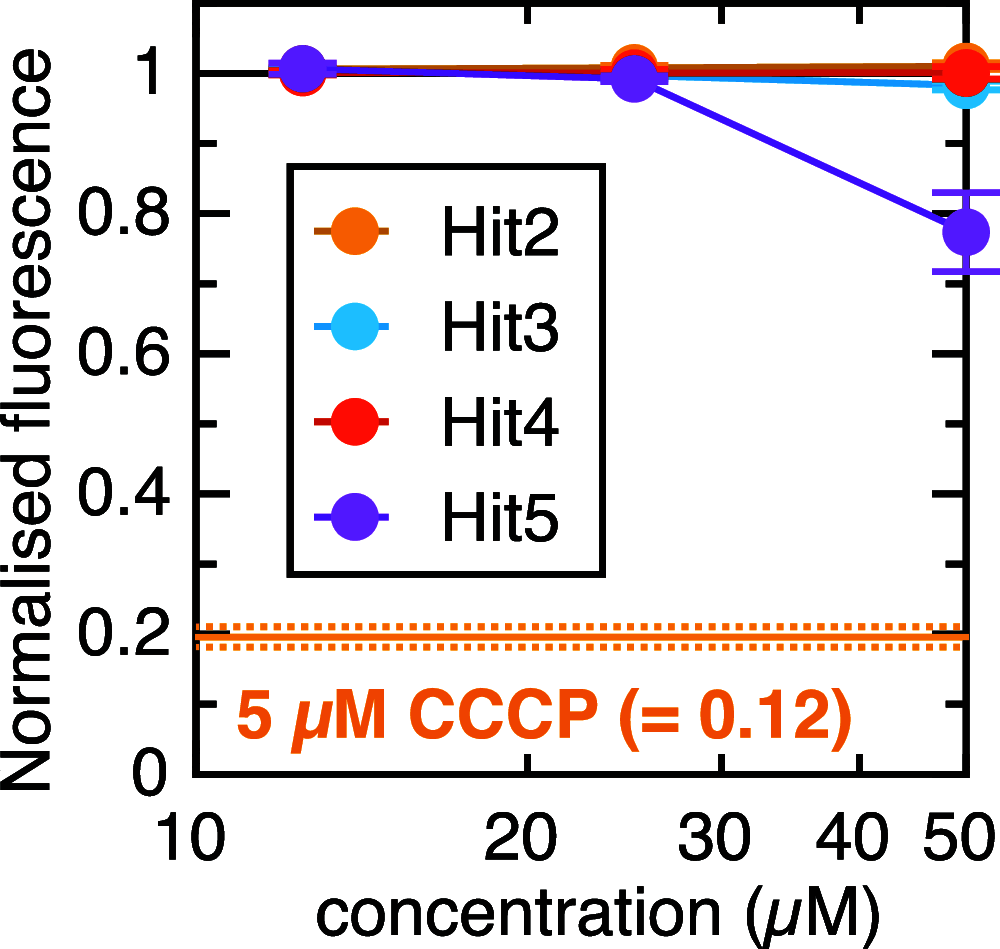
References
-
- Murray C. J. L.; Ikuta K. S.; Sharara F.; Swetschinski L.; Robles Aguilar G.; Gray A.; Han C.; Bisignano C.; Rao P.; Wool E.; Johnson S. C.; Browne A. J.; Chipeta M. G.; Fell F.; Hackett S.; Haines-Woodhouse G.; Kashef Hamadani B. H.; Kumaran E. A. P.; McManigal B.; Achalapong S.; Agarwal R.; Akech S.; Albertson S.; Amuasi J.; Andrews J.; Aravkin A.; Ashley E.; Babin F. X.; Bailey F.; Baker S.; Basnyat B.; Bekker A.; Bender R.; Berkley J. A.; Bethou A.; Bielicki J.; Boonkasidecha S.; Bukosia J.; Carvalheiro C.; Castañeda-Orjuela C.; Chansamouth V.; Chaurasia S.; Chiurchiù S.; Chowdhury F.; Clotaire Donatien R.; Cook A. J.; Cooper B.; Cressey T. R.; Criollo-Mora E.; Cunningham M.; Darboe S.; Day N. P. J.; De Luca M.; Dokova K.; Dramowski A.; Dunachie S. J.; Duong Bich T.; Eckmanns T.; Eibach D.; Emami A.; Feasey N.; Fisher-Pearson N.; Forrest K.; Garcia C.; Garrett D.; Gastmeier P.; Giref A. Z.; Greer R. C.; Gupta V.; Haller S.; Haselbeck A.; Hay S. I.; Holm M.; Hopkins S.; Hsia Y.; Iregbu K. C.; Jacobs J.; Jarovsky D.; Javanmardi F.; Jenney A. W. J.; Khorana M.; Khusuwan S.; Kissoon N.; Kobeissi E.; Kostyanev T.; Krapp F.; Krumkamp R.; Kumar A.; Kyu H. H.; Lim C.; Lim K.; Limmathurotsakul D.; Loftus M. J.; Lunn M.; Ma J.; Manoharan A.; Marks F.; May J.; Mayxay M.; Mturi N.; Munera-Huertas T.; Musicha P.; Musila L. A.; Mussi-Pinhata M. M.; Naidu R. N.; Nakamura T.; Nanavati R.; Nangia S.; Newton P.; Ngoun C.; Novotney A.; Nwakanma D.; Obiero C. W.; Ochoa T. J.; Olivas-Martinez A.; Olliaro P.; Ooko E.; Ortiz-Brizuela E.; Ounchanum P.; Pak G. D.; Paredes J. L.; Peleg A. Y.; Perrone C.; Phe T.; Phommasone K.; Plakkal N.; Ponce-de-Leon A.; Raad M.; Ramdin T.; Rattanavong S.; Riddell A.; Roberts T.; Robotham J. V.; Roca A.; Rosenthal V. D.; Rudd K. E.; Russell N.; Sader H. S.; Saengchan W.; Schnall J.; Scott J. A. G.; Seekaew S.; Sharland M.; Shivamallappa M.; Sifuentes-Osornio J.; Simpson A. J.; Steenkeste N.; Stewardson A. J.; Stoeva T.; Tasak N.; Thaiprakong A.; Thwaites G.; Tigoi C.; Turner C.; Turner P.; van Doorn H. R.; Velaphi S.; Vongpradith A.; Vongsouvath M.; Vu H.; Walsh T.; Walson J. L.; Waner S.; Wangrangsimakul T.; Wannapinij P.; Wozniak T.; Young Sharma T. E. M. W.; Yu K. C.; Zheng P.; Sartorius B.; Lopez A. D.; Stergachis A.; Moore C.; Dolecek C.; Naghavi M. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation 2021 Antibacterial agents in clinical and preclinical development: an overview and analysis; WHO; 2022
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

