Retinal perivascular macrophages regulate immune cell infiltration during neuroinflammation in mouse models of ocular disease
- PMID: 39207852
- PMCID: PMC11473146
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI180904
Retinal perivascular macrophages regulate immune cell infiltration during neuroinflammation in mouse models of ocular disease
Abstract
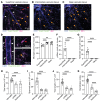
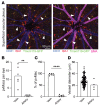
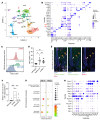
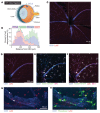
The blood-retina barrier (BRB), which is disrupted in diabetic retinopathy (DR) and uveitis, is an important anatomical characteristic of the retina, regulating nutrient, waste, water, protein, and immune cell flux. The BRB is composed of endothelial cell tight junctions, pericytes, astrocyte end feet, a collagen basement membrane, and perivascular macrophages. Despite the importance of the BRB, retinal perivascular macrophage function remains unknown. We found that retinal perivascular macrophages resided on postcapillary venules in the superficial vascular plexus and expressed MHC class II. Using single-cell RNA-Seq, we found that perivascular macrophages expressed a prochemotactic transcriptome and identified platelet factor 4 (Pf4, also known as CXCL4) as a perivascular macrophage marker. We used Pf4Cre mice to specifically deplete perivascular macrophages. To model retinal inflammation, we performed intraocular CCL2 injections. Ly6C+ monocytes crossed the BRB proximal to perivascular macrophages. Depletion of perivascular macrophages severely hampered Ly6C+ monocyte infiltration. These data suggest that retinal perivascular macrophages orchestrate immune cell migration across the BRB, with implications for inflammatory ocular diseases including DR and uveitis.
Keywords: Macrophages; Monocytes; Ophthalmology; Retinopathy.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

