Post-translational modifications in the Protein Data Bank
- PMID: 39207896
- PMCID: PMC11394121
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798324007794
Post-translational modifications in the Protein Data Bank
Abstract
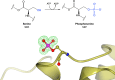
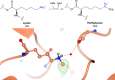
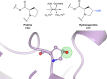
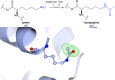
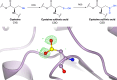
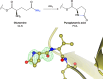
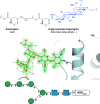
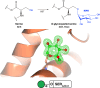
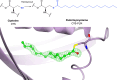
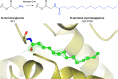
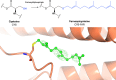
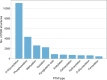
Proteins frequently undergo covalent modification at the post-translational level, which involves the covalent attachment of chemical groups onto amino acids. This can entail the singular or multiple addition of small groups, such as phosphorylation; long-chain modifications, such as glycosylation; small proteins, such as ubiquitination; as well as the interconversion of chemical groups, such as the formation of pyroglutamic acid. These post-translational modifications (PTMs) are essential for the normal functioning of cells, as they can alter the physicochemical properties of amino acids and therefore influence enzymatic activity, protein localization, protein-protein interactions and protein stability. Despite their inherent importance, accurately depicting PTMs in experimental studies of protein structures often poses a challenge. This review highlights the role of PTMs in protein structures, as well as the prevalence of PTMs in the Protein Data Bank, directing the reader to accurately built examples suitable for use as a modelling reference.
Keywords: Protein Data Bank; acetylation; glycosylation; phosphorylation; post-translational modifications.
open access.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in Prediction of Posttranslational Modification Sites Known to Localize in Protein Supersecondary Structures.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2870:117-151. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4213-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39543034
-
Post-translational modifications induce significant yet not extreme changes to protein structure.Bioinformatics. 2012 Nov 15;28(22):2905-13. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts541. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22947645
-
Post-translational modifications in drug resistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2025 Jan;78:101173. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2024.101173. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Drug Resist Updat. 2025. PMID: 39612546 Review.
-
Role of protein post-translational modifications in unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Sept 28;49(9):1495-1502. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240365. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39931779 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
-
Advances in post-translational modifications and recurrent spontaneous abortion.Gene. 2024 Nov 15;927:148700. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148700. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38880188 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of inflammation and protein carbamylation in patients with COVID-19.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 2;12:1561670. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1561670. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40241896 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for detecting, building, and improving tryptophan mannosylation in glycoprotein structures.Protein Sci. 2025 Feb;34(2):e70025. doi: 10.1002/pro.70025. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39840780 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Microwave Time on the Structure and Functional Properties of Glycosylated Soy 7S Globulins.Foods. 2025 Jan 7;14(2):151. doi: 10.3390/foods14020151. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39856821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam, R. M., Mukhopadhyay, N. K., Kim, J., Di Vizio, D., Cinar, B., Boucher, K., Solomon, K. R. & Freeman, M. R. (2007). Cancer Res.67, 6238–6246. - PubMed
-
- Agirre, J., Atanasova, M., Bagdonas, H., Ballard, C. B., Baslé, A., Beilsten-Edmands, J., Borges, R. J., Brown, D. G., Burgos-Mármol, J. J., Berrisford, J. M., Bond, P. S., Caballero, I., Catapano, L., Chojnowski, G., Cook, A. G., Cowtan, K. D., Croll, T. I., Debreczeni, J. É., Devenish, N. E., Dodson, E. J., Drevon, T. R., Emsley, P., Evans, G., Evans, P. R., Fando, M., Foadi, J., Fuentes-Montero, L., Garman, E. F., Gerstel, M., Gildea, R. J., Hatti, K., Hekkelman, M. L., Heuser, P., Hoh, S. W., Hough, M. A., Jenkins, H. T., Jiménez, E., Joosten, R. P., Keegan, R. M., Keep, N., Krissinel, E. B., Kolenko, P., Kovalevskiy, O., Lamzin, V. S., Lawson, D. M., Lebedev, A. A., Leslie, A. G. W., Lohkamp, B., Long, F., Malý, M., McCoy, A. J., McNicholas, S. J., Medina, A., Millán, C., Murray, J. W., Murshudov, G. N., Nicholls, R. A., Noble, M. E. M., Oeffner, R., Pannu, N. S., Parkhurst, J. M., Pearce, N., Pereira, J., Perrakis, A., Powell, H. R., Read, R. J., Rigden, D. J., Rochira, W., Sammito, M., Sánchez Rodríguez, F., Sheldrick, G. M., Shelley, K. L., Simkovic, F., Simpkin, A. J., Skubak, P., Sobolev, E., Steiner, R. A., Stevenson, K., Tews, I., Thomas, J. M. H., Thorn, A., Valls, J. T., Uski, V., Usón, I., Vagin, A., Velankar, S., Vollmar, M., Walden, H., Waterman, D., Wilson, K. S., Winn, M. D., Winter, G., Wojdyr, M. & Yamashita, K. (2023). Acta Cryst. D79, 449–461.
-
- Agirre, J., Davies, G. J., Wilson, K. S. & Cowtan, K. D. (2017). Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol.44, 39–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

