How Many Glucan Chains Form Plant Cellulose Microfibrils? A Mini Review
- PMID: 39207939
- PMCID: PMC11480985
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00995
How Many Glucan Chains Form Plant Cellulose Microfibrils? A Mini Review
Abstract
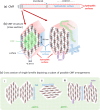
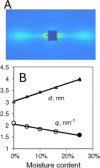
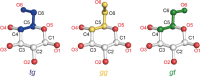
Assessing the number of glucan chains in cellulose microfibrils (CMFs) is crucial for understanding their structure-property relationships and interactions within plant cell walls. This Review examines the conclusions and limitations of the major experimental techniques that have provided insights into this question. Small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering data predominantly support an 18-chain model, although analysis is complicated by factors such as fibril coalescence and matrix polysaccharide associations. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy allows the estimation of the CMF width from the ratio of interior to surface glucose residues. However, there is uncertainty in the assignment of NMR spectral peaks to surface or interior chains. Freeze-fracture transmission electron microscopy images show cellulose synthase complexes to be "rosettes" of six lobes each consistent with a trimer of cellulose synthase enzymes, consistent with the synthesis of 18 parallel glucan chains in the CMF. Nevertheless, the number of chains in CMFs remains to be conclusively demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nishiyama Y. Structure and properties of the cellulose microfibril. J. Wood Sci. 2009, 55, 241–9. 10.1007/s10086-009-1029-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

