Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men and transgender women in Belgium: awareness, use and antimicrobial resistance concerns in a cross-sectional online survey
- PMID: 39209541
- PMCID: PMC11877044
- DOI: 10.1136/sextrans-2024-056261
Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men and transgender women in Belgium: awareness, use and antimicrobial resistance concerns in a cross-sectional online survey
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to assess the awareness, willingness to use and use of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxyPEP) among men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women (TGW) in Belgium. Additionally, we aimed to identify factors associated with doxyPEP use and concerns regarding antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Methods: Cross-sectional online survey among MSM and TGW in Belgium in April 2024. Participants were recruited through sexual networking applications and social media of community-based organisations. Numerical variables were compared with Wilcoxon rank-sum test and categorical variables with χ2 or Fisher's exact tests. Factors associated with doxyPEP use were assessed using logistic regression. Willingness to use doxyPEP and concerns about side effects/AMR were assessed before and after presenting a brief paragraph on the potential effects of doxyPEP on AMR.
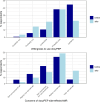
Results: 875 individuals initiated the survey. Almost all identified as men (860/875, 98.3%) with a median age of 40 years (IQR 32-48), 40.4% (n=352/875) had heard of doxyPEP and 9.4% (n=82/875) had used it, among whom the majority used it within the previous 6 months (70/81, 86.4%). In multivariable logistic regression, doxyPEP use was associated with reporting ≥1 sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the previous 12 months, engagement in chemsex, HIV status and pre-exposure prophylaxis use, and education level.About 80% of the participants initially reported being willing to use doxyPEP, and about 50% reported being concerned about side effects. After reading about the potential effects of doxyPEP on AMR, willingness to use decreased to 60% and concerns of side effects/AMR increased to around 70%.
Conclusions: Approximately 1 in 10 MSM in Belgium reported using doxyPEP. A recent history of STIs and STI risk factors were positively associated with doxyPEP use. Importantly, concerns about AMR and side effect influenced willingness to use doxyPEP. If doxyPEP is introduced, informing patients about doxyPEP benefits and risks is crucial to enable informed decision-making.
Keywords: Antibiotic Prophylaxis; Chlamydia Infections; Gonorrhea; Post-Exposure Prophylaxis; SYPHILIS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Molina J-M, Charreau I, Chidiac C, et al. Post-exposure prophylaxis with doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men: an open-label randomised substudy of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18:308–17. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30725-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Molina J-M, Bercot B, Assoumou L, et al. ANRS 174 DOXYVAC: an open-label randomized trial to prevent STIs in MSM on PrEP (CROI abstract 119) Top Antivir Med. 2023;31:49
-
- Molina J-M, Bercot B, Assoumou L, et al. Doxycycline prophylaxis and meningococcal group B vaccine to prevent bacterial sexually transmitted infections in France (ANRS 174 DOXYVAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial with a 2 × 2 factorial design. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00236-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous