Characteristics of blood-brain barrier heterogeneity between brain regions revealed by profiling vascular and perivascular cells
- PMID: 39210068
- PMCID: PMC11452347
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01743-y
Characteristics of blood-brain barrier heterogeneity between brain regions revealed by profiling vascular and perivascular cells
Abstract
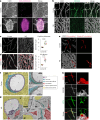
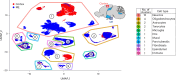
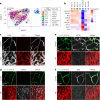
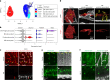
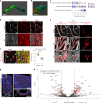
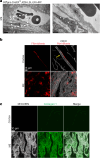
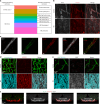
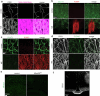
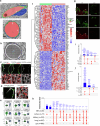
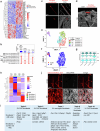
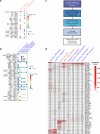
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the brain and maintains neuronal homeostasis. BBB properties can vary between brain regions to support regional functions, yet how BBB heterogeneity occurs is poorly understood. Here, we used single-cell and spatial transcriptomics to compare the mouse median eminence, one of the circumventricular organs that has naturally leaky blood vessels, with the cortex. We identified hundreds of molecular differences in endothelial cells (ECs) and perivascular cells, including astrocytes, pericytes and fibroblasts. Using electron microscopy and an aqueous-based tissue-clearing method, we revealed distinct anatomical specializations and interaction patterns of ECs and perivascular cells in these regions. Finally, we identified candidate regionally enriched EC-perivascular cell ligand-receptor pairs. Our results indicate that both molecular specializations in ECs and unique EC-perivascular cell interactions contribute to BBB functional heterogeneity. This platform can be used to investigate BBB heterogeneity in other regions and may facilitate the development of central nervous system region-specific therapeutics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kaur, C. & Ling, E.-A. The circumventricular organs. Histol. Histopathol.32, 879–892 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DP1 NS092473/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1DA048786/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- P30 NS072030/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35NS116820/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- RF1 DA048786/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026866/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- Investigator/Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
- R35 NS116820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS108410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD105351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS085320/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DRG-2289-17/Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (Cancer Research Fund of the Damon Runyon-Walter Winchell Foundation)
- DP1NS092473/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- ALTF 42-2017/European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO)
- Faculty Scholar/Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

