Human genomic DNA is widely interspersed with i-motif structures
- PMID: 39210146
- PMCID: PMC11480443
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00210-5
Human genomic DNA is widely interspersed with i-motif structures
Abstract
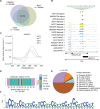
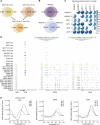
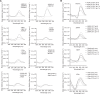
DNA i-motif structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells and are believed to provide critical genomic regulation. While the existence, abundance, and distribution of i-motif structures in human cells has been demonstrated and studied by immunofluorescent staining, and more recently NMR and CUT&Tag, the abundance and distribution of such structures in human genomic DNA have remained unclear. Here we utilise high-affinity i-motif immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing to map i-motifs in the purified genomic DNA of human MCF7, U2OS and HEK293T cells. Validated by biolayer interferometry and circular dichroism spectroscopy, our approach aimed to identify DNA sequences capable of i-motif formation on a genome-wide scale, revealing that such sequences are widely distributed throughout the human genome and are common in genes upregulated in G0/G1 cell cycle phases. Our findings provide experimental evidence for the widespread formation of i-motif structures in human genomic DNA and a foundational resource for future studies of their genomic, structural, and molecular roles.
Keywords: Antibody; DNA Quadruplex Structures; Immunoprecipitation; i-motif; iMab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Andrews S (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

