A CCL2/MCP-1 antagonist attenuates fibrosis of the infrapatellar fat pad in a rat model of arthritis
- PMID: 39210303
- PMCID: PMC11360299
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-024-07737-y
A CCL2/MCP-1 antagonist attenuates fibrosis of the infrapatellar fat pad in a rat model of arthritis
Abstract
Background: Fibrosis of the infrapatellar fat pad (IFP) is a feature of osteoarthritis and contributes substantially to the pain and dysfunction in patients' joints. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. C-C motif chemokine ligand-2 (CCL2) plays a central role in tissue fibrosis. Thus, we aimed to investigate the role of CCL2 in the development of IFP fibrosis in a rat model of arthritis, hypothesizing that a CCL2 antagonist could mitigate fibrotic progression.
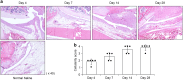
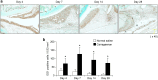
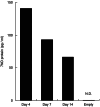
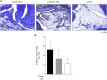
Methods: We induced arthritis in male Wistar rats using intra-articular injections of carrageenan. Furthermore, to evaluate the effects of a CCL2 antagonist on protein expression and collagen deposition in the IFP of the rats, we transferred an N-terminal-truncated CCL2 gene into a rat model via electroporation-mediated intramuscular injection. Macrophage infiltration and collagen deposition in the IFP were analyzed in vivo. Groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test and Student's t-test.
Results: We identified infiltrating macrophages as well as increases in CCL2 and TGF-β levels as collagen deposition progressed. Gene transfer of the CCL2-antagonist before arthritis induction attenuated collagen deposition remarkably.
Conclusions: We provide initial evidence that anti-CCL2 gene therapy can effectively suppress the development of IFP fibrosis in a rat model. Thus, targeting CCL2 holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for managing tissue fibrosis in osteoarthritis patients.
Keywords: CCL2; Fibrosis; Gene therapy; Infrapatellar fat pad; Macrophages; Osteoarthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Nakagawa Y, Tsuji K, Nakamura T, Katagiri H, Ozeki N, Shioda M, An JS, Yoshida R, Sekiya I, Koga H. Association of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Fibrosis at 3 months after ACL Reconstruction with short-term clinical outcomes and inflammatory cytokine levels in the synovial fluid. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(4). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eymard F, Pigenet A, Citadelle D, Flouzat-Lachaniette CH, Poignard A, Benelli C, et al. Induction of an inflammatory and prodegradative phenotype in autologous fibroblast-like synoviocytes by the infrapatellar fat pad from patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:2165–74. 10.1002/art.38657 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

