Prognostic significance and treatment strategies for IKZF1 deletion in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 39210321
- PMCID: PMC11363382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12828-z
Prognostic significance and treatment strategies for IKZF1 deletion in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Background: The predictive importance of IKZF1del in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) has shown variability across different studies. Thus, the optimal treatment approach for children with IKZF1del BCP-ALL remains contentious, with the ongoing debate surrounding the use of IKZF1del-based high-risk stratification versus a minimal residual disease (MRD)-guided protocol.
Methods: IKZF1 status was reliably determined in 804 patients using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) data obtained from four hospitals in Fujian, a province of China. In the Chinese Children Leukemia Group (CCLG)-ALL 2008 cohort, IKZF1 status was included in the risk assignment, with all IKZF1del patients receiving a high-risk regimen. Conversely, in the Chinese Children's Cancer Group (CCCG)-ALL 2015 cohort, IKZF1del was not incorporated into the risk assignment, and patients were treated based on an MRD-guided risk stratification protocol.
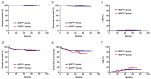
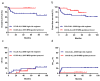
Results: IKZF1del was found in 86 patients (86/804, 10.7%) overall and in 30 (30/46, 65.2%) BCR::ABL1-positive patients. Overall, IKZF1del was a poor prognostic predictor for patients, though the significance diminished upon age adjustment, white blood cell (WBC) count at diagnosis, treatment group, and MRD status. In the CCLG-ALL 2008 cohort, IKZF1del conferred a notably lower 5-year overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) and a significantly higher 5-year cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) than IKZF1wt. In the CCLG-ALL 2015 cohort, IKZF1del conferred a lower 5-year OS and EFS and a higher 5-year CIR than IKZF1wt, but the differences were insignificant. The IKZF1del patients treated with higher intensity chemotherapy (CCLG-ALL 2008 high-risk regimen) had a markedly lower 5-year OS and EFS compared with those treated with the MRD-guided protocol (CCCG-ALL 2015 protocol). Furthermore, patients treated with the CCLG-ALL 2008 high-risk regimen experienced a higher frequency of serious adverse events (SAEs), especially infection-related SAEs, compared with those treated with the CCCG-ALL 2015 MRD-guided protocol.
Conclusions: The prognostic effect of IKZF1del may vary in different protocols. Compared with higher intensity chemotherapy, the MRD-guided protocol may be a more effective approach to treating BCP-ALL with IKZF1del in children.
Keywords: IKZF1 deletion; Minimal residual disease-guided protocol; Pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Pui CH, Pei D, Coustan-Smith E, Jeha S, Cheng C, Bowman WP, et al. Clinical utility of sequential minimal residual disease measurements in the context of risk-based therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:465–74. 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70082-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Cai J, Shen S, Gao J, Yu J, Hu S, et al. Pulse therapy with vincristine and dexamethasone for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (CCCG-ALL-2015): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1322–32. 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00328-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021QH1049/Startup Fund for Scientific Research, Fujian Medical University
- 2021-76/National Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of China
- 2020Y2006/Fujian Provincial Clinical Research Center for Hematological Malignancies
- 2020Y9052/Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

