Gender-specific associations among neck circumference, the rs9939609 FTO gene polymorphism, and the 14-year risk of metabolic syndrome in the Korean adult population
- PMID: 39210785
- PMCID: PMC11826040
- DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2024072
Gender-specific associations among neck circumference, the rs9939609 FTO gene polymorphism, and the 14-year risk of metabolic syndrome in the Korean adult population
Abstract
Objectives: Limited data exist on the relation between neck circumference (NC) and the risk of developing metabolic syndrome (MS). This study investigated gender-specific associations between NC and the 14-year risk of MS and explored the impact of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism on these associations.
Methods: This population-based prospective cohort study involved 2,666 participants (1,301 men and 1,365 women), who were free of MS at baseline (2005-2006). Incident MS cases, defined by the presence of 3 or more criteria regarding blood pressure and blood levels of glucose, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, were identified through biennial examinations until 2020. NC measurements taken at baseline and between 2013 and 2014 were analyzed using Cox proportional hazard regression to determine gender-specific associations with MS risk.
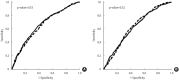
Results: Controlling for potential confounders such as waist circumference (WC), significant associations were observed in both genders. Individuals in the highest NC quartile exhibited more than a 2-fold higher MS risk than those in the lowest quartile; with hazard ratios of 2.37 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.74 to 3.22) for men and 2.65 (95% CI, 1.89 to 3.72) for women (p for trend <0.001). No significant interaction was found between the FTO polymorphism and NC. In diagnostic test analyses, NC and WC demonstrated comparable area under the curve values in both genders.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that NC is as effective as WC for predicting the incidence of MS.
Keywords: FTO; Incidence; Metabolic syndrome; Neck; Waist circumference.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare for this study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

