Current Approaches to Prevent or Reverse Microbiome Dysbiosis in Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases
- PMID: 39211023
- PMCID: PMC11350408
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.240224.cap
Current Approaches to Prevent or Reverse Microbiome Dysbiosis in Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
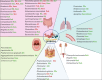
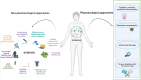
Advances in knowledge of the microbiome and its relationship with the immune system have led to a better understanding of the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases (CIRD). Indeed, the microbiome dysbiosis now occupies a particular place with implications for the determinism and clinical expression of CIRD, as well as the therapeutic response of affected patients. Several approaches exist to limit the impact of the microbiome during CIRD. This review aimed to present current strategies to prevent or reverse microbiome dysbiosis based on existing knowledge, in order to provide practical information to healthcare professionals treating patients suffering from CIRD.
Keywords: chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases; dysbiosis; microbiome; prevention; sub-Saharan Africa; treatment.
© 2024 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moutsopoulos HM. Autoimmune rheumatic diseases: One or many diseases? J Transl Autoimmun [Internet] 28 oct 2021;4. Disponible sur: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8716565/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vural M, Gilbert B, Üstün I, Caglar S, Finckh A. Mini-Review: Human Microbiome and Rheumatic Diseases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol [Internet] 10 nov 2020;10. Disponible sur: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7693548/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ford B. The story of the simple microscope: Heinemann. 1985;
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
