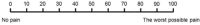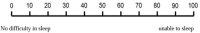Multifactorial Nature of Fatigue in North Indian Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 39211025
- PMCID: PMC11350424
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.150124.mnf
Multifactorial Nature of Fatigue in North Indian Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
Introduction: Fatigue is a common, disabling, and poorly understood aspect of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. Better understanding of fatigue is required for holistic treatment of RA. The present study was conducted to evaluate factors (disease activity, pain, sleep quality, and vitamin D) contributing to fatigue in RA.
Method: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 204 patients of RA. Fatigue was measured using CFQ-11 scale, pain and sleep impairment were assessed on visual analogue scale, disease activity by DAS 28 ESR, and vitamin D levels by enzyme chemiluminescence immunoassay. Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses were done to study association.
Results: Mean age of study subjects was 51±11.63 years with majority (89.7%) being females and mean duration of RA was 8.54 years. Prevalence of fatigue was 66.2% (CFQ-11 score >4/11). Deficiency of vitamin D was found in 12.3% subjects. Mean sleep impairment and pain score on VAS were 32.60±21.53 and 26.37±21.65 respectively. Univariate analysis revealed that CFQ-11 fatigue score was independently associated with disease activity, pain, sleep, and vitamin D deficiency. Further Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis showed strongest association of vitamin D deficiency with fatigue (OR of 6.38 with 95% confidence interval of 1.58, 25.71). Disease activity (OR - 1.714, 95% CI- 1.14, 2.55) and sleep impairment (OR - 1.038, 95% CI- 1.005, 1.071) have also been found to be significantly associated with fatigue.
Conclusion: Fatigue in RA is multifactorial, and it is mediated by disease-related factors (disease activity, sleep impairment) and non-disease-related factors (vitamin D deficiency).
Keywords: disease activity; fatigue; pain; rheumatoid arthritis; sleep quality; vitamin D.
© 2024 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Association between vitamin D and fatigue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2020 Feb 6;10(2):e034935. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-034935. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32034029 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep disorders in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with quality of life, fatigue, depression levels, functional disability, disease duration, and activity: a multicentre cross-sectional study.J Int Med Res. 2023 Oct;51(10):3000605231204477. doi: 10.1177/03000605231204477. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37818729 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep disturbance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is related to fatigue, disease activity, and other patient-reported outcomes.Scand J Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;46(2):95-103. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2016.1168482. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27319613
-
The Assessment of Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Its Impact on Their Quality of Life.Clin Pract. 2022 Jul 26;12(4):591-598. doi: 10.3390/clinpract12040062. Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35892448 Free PMC article.
-
European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new Patient Reported Outcome questionnaire (D-PRO).Autoimmun Rev. 2017 May;16(5):548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28279841 Review.
References
-
- Brooks PM. Rheumatoid arthritis: aetiology and clinical features. Medicine 2006;34(10):379–82. 10.1053/j.mpmed2006.07.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous