Expression Levels and Clinical Values of miR-195, miR-424, miR-10b, miR-103a-3p, and miR-542-3p in Vasculo-Behçet's Disease
- PMID: 39211027
- PMCID: PMC11350416
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.030623.elc
Expression Levels and Clinical Values of miR-195, miR-424, miR-10b, miR-103a-3p, and miR-542-3p in Vasculo-Behçet's Disease
Abstract
Objective: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in a range of pathological and biological processes. Vascular involvement is an important complication associated with morbidity and mortality in Behçet's disease (BD). In this study, we aimed to evaluate the expression levels of miR-195, miR-424, miR-10b, miR-103a-3p, and miR-542-3p in Turkish patients with BD, and their possible association with vascular involvement and clinical activity.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 61 BD patients and 25 age- and sex-matched healthy individuals. The patients were categorised into two groups based on the presence or absence of vascular involvement. Demographic data, disease duration, disease activity, and medical treatments were recorded. Disease activity was evaluated using the Behçet's Disease Current Activity Form (BDCAF) and the Behçet's Syndrome Activity Scale (BSAS). The expression levels of miRNAs were measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR).
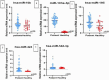
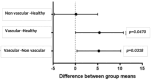
Results: The comparison of the clinical features of BD patients with and without vascular involvement revealed no significant difference. However, the expression levels of miR-195, miR-424, miR-10b, miR-103a-3p, and miR-542-3p were significantly higher in BD patients than in healthy controls (p<0.001, p<0.001, p=0.010, p<0.01, p=0.039, respectively). Moreover, the expression level of miR-195 was significantly higher in vasculo-Behçet patients than in the other groups (p=0.0318). However, no significant association was found between the expression levels of miR-195 and clinical activity.
Conclusion: Our study results indicated elevated serum levels of miR-195 in BD patients, which may be associated with vascular involvement. Therefore, miR-195 could potentially serve as a biomarker for the diagnosis and monitoring of vasculo-Behçet's disease.
Keywords: Behçet’s disease; microRNA-195; real-time quantitative PCR; serum.
© 2024 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with Behçet's disease: do their higher levels correlate to vasculo-Behçet's disease associated with aneurysm formation?Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007 Jul-Aug;25(4 Suppl 45):S70-5. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17949555
-
Ultrasonographic measurement of the vascular wall thickness and intima-media thickness in patients with Behçet's disease with symptoms or signs of vascular involvement: A cross-sectional study.Arch Rheumatol. 2021 Jan 14;36(2):258-266. doi: 10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2021.8423. eCollection 2021 Jun. Arch Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34527931 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of miR-127 and miR-29 in Egyptian patients with Behçet disease and its clinical significance and relationship with disease activity.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jun;44(6):2439-2445. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07470-4. Epub 2025 May 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40360903 Free PMC article.
-
[Vasculo-Behçet's disease].Nihon Rinsho. 1994 Aug;52(8):2138-42. Nihon Rinsho. 1994. PMID: 7933600 Review. Japanese.
-
Effectiveness of tocilizumab in Behcet's disease: A systematic literature review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Aug;50(4):797-804. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.05.017. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32544751
Cited by
-
Behçet's Disease with Intestinal Involvement can be Distinguished from Inflammatory Bowel Diseases by Measurement of Common Femoral Vein Wall Thickness.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025 May 28;36(2):268-272. doi: 10.31138/mjr.120824.dfh. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40757131 Free PMC article.
-
AhR Activation at the Air-Blood Barrier Alters Systemic microRNA Release After Inhalation of Particulate Matter Containing Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 May;25(5):651-665. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-09989-z. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40214911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bettiol A, Prisco D, Emmi G. Behçet: the syndrome. Rheumatology 2020;59:101–7. - PubMed
-
- Alipour S, Nouri M, Khabbazi A, Samadi N, Babaloo Z, Abolhasani S, et al. Hypermethylation of IL-10 gene is responsible for its low mRNA expression in Behçet’s disease. J Cell Biochem 2018;119:6614–22. - PubMed
-
- Emmi G, Bettiol A, Silvestri E, Di Scala G, Becatti M, Fiorillo C, et al. Vascular Behçet’s syndrome: an update. Intern Emerg Med 2019;14(5):645–52. - PubMed
-
- Ishigatsubo Y. [Statement draft for clinical guidelines of vasculo-Behçet’s Disease]. [Internet]. 2014. http://www.nanbyou.or.jp/upload_files/Bechet2014_4.pdf [cited 2018 Jun. 6] Available from: (in Japanese).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources