Targeting amino acid-metabolizing enzymes for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 39211039
- PMCID: PMC11359565
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1440269
Targeting amino acid-metabolizing enzymes for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
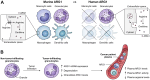
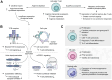
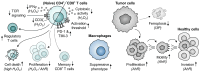
Despite the immune system's role in the detection and eradication of abnormal cells, cancer cells often evade elimination by exploitation of various immune escape mechanisms. Among these mechanisms is the ability of cancer cells to upregulate amino acid-metabolizing enzymes, or to induce these enzymes in tumor-infiltrating immunosuppressive cells. Amino acids are fundamental cellular nutrients required for a variety of physiological processes, and their inadequacy can severely impact immune cell function. Amino acid-derived metabolites can additionally dampen the anti-tumor immune response by means of their immunosuppressive activities, whilst some can also promote tumor growth directly. Based on their evident role in tumor immune escape, the amino acid-metabolizing enzymes glutaminase 1 (GLS1), arginase 1 (ARG1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) and interleukin 4 induced 1 (IL4I1) each serve as a promising target for immunotherapeutic intervention. This review summarizes and discusses the involvement of these enzymes in cancer, their effect on the anti-tumor immune response and the recent progress made in the preclinical and clinical evaluation of inhibitors targeting these enzymes.
Keywords: IDO1; IL4I1; amino acid metabolism; arginine; cancer immunotherapy; glutamine; immunosuppression; tryptophan.
Copyright © 2024 Grobben.
Conflict of interest statement
Author YG was employed by Oncolines B.V.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Modulation of cancer-specific immune responses by amino acid degrading enzymes.Immunotherapy. 2017 Jan;9(1):83-97. doi: 10.2217/imt-2016-0118. Immunotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28000524 Review.
-
Tryptophan: A Rheostat of Cancer Immune Escape Mediated by Immunosuppressive Enzymes IDO1 and TDO.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:636081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636081. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Pathways: Targeting IDO1 and Other Tryptophan Dioxygenases for Cancer Immunotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;21(24):5427-33. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0420. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26519060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Targeting Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases and Tryptophan Dioxygenase for Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 6;12:789473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.789473. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34938297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting Indoleamine Dioxygenase and Tryptophan Dioxygenase in Cancer Immunotherapy: Clinical Progress and Challenges.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Aug 8;16:2639-2657. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S373780. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35965963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated neutrophils in tumor treatment and therapeutic resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 24;13:1584987. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1584987. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40342932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of circulating immuno-oncology biomarkers with breast cancer risk: insights from two prospective cohorts.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Jul 15;9(1):238. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-01019-z. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40665092 Free PMC article.
-
Defeating lethal cancer: Interrupting the ecologic and evolutionary basis of death from malignancy.CA Cancer J Clin. 2025 May-Jun;75(3):183-202. doi: 10.3322/caac.70000. Epub 2025 Mar 9. CA Cancer J Clin. 2025. PMID: 40057846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Salivary Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer by Integrating Olink Proteomics and Metabolomics.J Proteome Res. 2025 May 2;24(5):2542-2552. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00091. Epub 2025 Apr 4. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40183281
-
Amino acid-based risk stratification model improves prognostic precision in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jun 21;25(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03879-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40544249 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

