Dysregulated gene expression of SUMO machinery components induces the resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in lung cancer by upregulating the death of peripheral blood lymphocytes
- PMID: 39211047
- PMCID: PMC11357960
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424393
Dysregulated gene expression of SUMO machinery components induces the resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in lung cancer by upregulating the death of peripheral blood lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: The majority of patients with lung cancer exhibit drug resistance after anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, leading to shortened patient survival time. Previous studies have suggested an association between epigenetic abnormalities such as methylation and clinical response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, while the role of SUMOylation in resistance to anti-PD-1 antibody immunotherapy is still unclear.
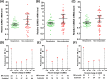
Methods: Here, the mRNA expression of 15 SUMO machinery components in PBMC from lung cancer patients receiving anti-PD-1 immunotherapy were analyzed using real-time PCR. Base on the percentage change in mRNA levels, the relationship between the expression of SUMO machinery components and outcomes of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, and the influencing factors of SUMOylation were evaluated. PBMC was treated with different concentrations of 2-D08 (a specific inhibitor of SUMOylation) in vitro, and analyzed the activation and the death rates of lymphocyte subsets by flow cytometry analysis.
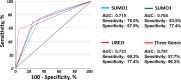
Results: A predictive method, base on the gene expression of three SUMO machinery components (SUMO1, SUMO3 and UBE2I), were developed to distinguish non-responders to PD-1 inhibitors. Furthermore, the number of lymphocytes in peripheral blood significantly reduced in the dysregulated SUMOylation groups (the percentage change >100 or -50 ~ -100 groups). In vitro studies confirmed that lightly low SUMOylation level improved the activation status of T and NK lymphocytes, but extremely low SUMOylation level lead to the increased death rates of lymphocytes.
Conclusion: Our findings implied that dysregulated gene expression of SUMO machinery components could induce the resistance of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in lung cancer by upregulating the death of peripheral blood lymphocytes. These data might provide effective circulating biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, and uncovered a novel regulatory mechanism of resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD-1; Sumoylation; lymphocyte; peripheral blood; resistance.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Sun, Liu, Xu, Li, Zhang and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
EGFR mutations induce the suppression of CD8+ T cell and anti-PD-1 resistance via ERK1/2-p90RSK-TGF-β axis in non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 14;22(1):653. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05456-5. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39004699 Free PMC article.
-
CD161+CD127+CD8+ T cell subsets can predict the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with diabetes mellitus.Oncoimmunology. 2024 Jun 27;13(1):2371575. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2371575. eCollection 2024. Oncoimmunology. 2024. PMID: 38952673 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in circulating PD-1+CD8+ T lymphocytes for predicting treatment response to PD-1 blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Jan;143:113-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.10.028. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33302114
-
Immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harbouring driver mutations.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 May;96:102179. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102179. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 33798954 Review. No abstract available.
-
Study and analysis of antitumor resistance mechanism of PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blocker.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(21):8086-8121. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3410. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32875727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marei HE, Hasan A, Pozzoli G, Cenciarelli C. Cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs): potential, mechanisms of resistance, and strategies for reinvigorating T cell responsiveness when resistance is acquired. Cancer Cell Int. (2023) 23:64. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02902-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai X, Kim M, Kasumova G, Si L, Tang B, Cui C, et al. . Radiological dynamics and SITC-defined resistance types of advanced melanoma during anti-PD-1 monotherapy: an independent single-blind observational study on an international cohort. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002092. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

