Therapy of IgA nephropathy: time for a paradigm change
- PMID: 39211339
- PMCID: PMC11358106
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1461879
Therapy of IgA nephropathy: time for a paradigm change
Abstract
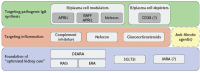
Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) often has a poor outcome, with many patients reaching kidney failure within their lifetime. Therefore, the primary goal for the treatment of IgAN should be to reduce nephron loss from the moment of diagnosis. To achieve this, IgAN must be recognized and treated as both a chronic kidney disease and an immunological disease. Agents that have received US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency approval for the treatment of IgAN include modified-release/targeted-release formulation budesonide (Nefecon) and sparsentan, a selective dual endothelin-A and angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist. Other agents, including selective endothelin receptor antagonists, selective or combined APRIL and BAFF antagonists, and a vast array of complement inhibitors are being investigated for the treatment of IgAN. Furthermore, treatment combinations are also being studied, including sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors with endothelin receptor antagonists. Due to the complexity of IgAN, combination treatment, rather than a single-agent approach, may provide maximum benefit. With the number of treatments for IgAN likely to increase, combinations allowing safe and effective treatment to halt progression to kidney failure seem within grasp. While trials evaluating combinations are ongoing, more are needed to pave the way for a comprehensive IgAN treatment strategy. Furthermore, an approach to IgAN treatment in which agents are combined early to achieve rapid induction of remission and prevent unnecessary and irreversible nephron loss is required. Following remission, treatments may be adjusted and stripped back as necessary in the maintenance phase with close monitoring. This review discusses the current status of IgAN treatment and explores future strategies to improve outcomes for patients with IgAN.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; SGLT2 inhibitor; budesonide; eGFR; glucocorticoids; nephron; proteinuria; sparsentan.
Copyright © 2024 Barratt, Lafayette and Floege.
Conflict of interest statement
JB is a consultant for Alebund, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Alpine, Argenx, Astellas, BioCryst, Calliditas, Chinook, Dimerix, HiBio, Kira, Novartis, Omeros, Otsuka, Q32 Bio, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, Travere Therapeutics, Vera Therapeutics, CSL Vifor, and Visterra; has received research funding from Argenx, Calliditas, Chinook, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Omeros, Travere Therapeutics, and Visterra; has roles on the Editorial Boards of CJASN, Clinical Science, Glomerular Diseases, and Kidney International; has an advisory or leadership role as Treasurer of International IgA Nephropathy Network. JF is a Senior Professor at the RWTH Aachen University Hospital; is a consultant for Calliditas, Chinook, Omeros, Travere, Novartis, Bayer, AstraZeneca, CSL Vifor and Fresenius; has received honoraria from Calliditas, Omeros, Otsuka, GSK, Travere, Novartis, Bayer, AstraZeneca, CSL Vifor and Fresenius; and is a member of data safety monitoring boards of Novo Nordisk and Visterra. RL is a consultant for Omeros, Calliditas, Travere, Vera, Apellis, Otsuka, Visterra, Novartis, Alexion and Chinook; has received research grants from Omeros, Calliditas, Travere, Vera, Apellis, Otsuka, Visterra, and Chinook; and has received support for travel or attending meetings from Calliditas and Otsuka. All authors are members of the Academic Leadership Committee for the Narsoplimab in IgAN Drug Development Programme. CSL Vifor participated in preparation and review of the manuscript, and the decision to submit the article for publication.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

