Leadership shift in the global soybean market: Dynamic connectedness approach (TVP-VAR)
- PMID: 39211921
- PMCID: PMC11357759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36071
Leadership shift in the global soybean market: Dynamic connectedness approach (TVP-VAR)
Abstract
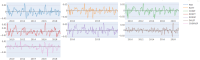
The price transmission in international soybean market has been extensively examined. However, recent econometric advancements have enabled the application of dynamic connectedness methodology as outlined by Antonakakis and Gabauer (2017) [1], which is based on a Time-varying Parameter Vector Autoregressive (TVP-VAR) model. This approach captures the time-varying connectedness of time series, considering potential risk shock emitters and receivers. The connectedness index (Diebold and Yilmaz, Jan. 2012) [2] was developed using Generalized Forecast Error Variance Decomposition (GFEVD) and the Generalized Impulse Response Function (GIRF) (Koop et al., Sep. 1996; Pesaran and Shin, Jan. 1998) [3,4]. This study aims to understand the dynamic connectedness and price leadership. The research examined markets including the US Soybean futures market (Chicago Board of Trade), Rotterdam Port spot market representing the European soybean market, Paranaguá port representing Brazil, Argentina represented by Rosario Futures and Spot, and the Chinese domestic spot market and the Dalian futures on behalf of China. The research spanned approximately ten years, from September 2009 to May 2019. The findings suggest that the soybean market has reached a high level of maturity, able to withstand exogenous shocks for at least the past seven years. The net pairwise directional connectedness revealed dynamic and bidirectional causality. The dynamic connectedness index showed a highly connected and developed market in the West (Chicago Futures, Rotterdam, Paranaguá, and Rosario Futures and Spot). However, the connectedness between Western and Eastern markets was relatively low, indicating some level of market isolation. Furthermore, the pairwise connectedness index between Eastern market (China spot and Dalian Futures) was also considerable low. Lastly, Paranaguá and Rosario overtook Rotterdam as price-leading markets and were identified as the primary net transmitters of shocks, indirectly implying causality. Chicago, Rosario, and Paranaguá formed a triumvirate leading international prices, while Rotterdam adopted a secondary leading position, deviating from its historical role as the price leader.
Keywords: AI Deep Economics; Connectedness approach; Connectedness index; International soybean market; Price transmission; Risk of spillover; TVP-VAR.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Gustavo Barboza Martignone reports writing assistance was provided by Harper Adams University College Department of Land Farm and Agribusiness Management.
Figures
References
-
- Antonakakis N., Gabauer D. Refined measures of dynamic connectedness based on TVP-VAR. Mpra. 2017;78282(78282):1–15.
-
- Diebold F.X., Yilmaz K. Better to give than to receive: predictive directional measurement of volatility spillovers. Int. J. Forecast. Jan. 2012;28(1):57–66.
-
- Barboza Martignone G., Behrendt K., Paparas D. Price transmission analysis of the international soybean market in a trade war context. Economies. 2022;10(8):203.
-
- McCorriston S., Morgan W., Rayner J. Price transmission, market power, marketing chain, returns to scale, food industry. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. Jan. 2001;28(2):143–159.
-
- Meyer J., von Cramon-Taubadel S. Asymmetric price transmission: a survey. J. Agric. Econ. 2004;55(3):581–611.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous