Effect of GBA1 Mutations and APOE Polymorphisms on Survival and Progression Among Ashkenazi Jews with Dementia with Lewy Bodies
- PMID: 39212252
- PMCID: PMC11657010
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.30003
Effect of GBA1 Mutations and APOE Polymorphisms on Survival and Progression Among Ashkenazi Jews with Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Abstract
Background: Glucocerebrosidase 1 (GBA1) mutations are associated with reduced survival in Parkinson's disease but their effect on survival in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is unclear.
Objective: To assess the impact of GBA1 mutations on survival among Ashkenazi Jews with DLB, while controlling for APOE status.
Methods: One hundred and forty participants from Tel Aviv Medical Center, Israel were genotyped for GBA1 mutations and APOE polymorphisms. Survival rates and follow-up cognitive screening scores were analyzed.
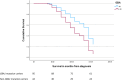
Results: GBA1 mutation carriers had a two-fold increased risk of death (HR = 1.999), while APOE status did not independently affect survival. In a subset of patients with available clinical data (N = 63), carriers of the APOE ε4 allele showed faster cognitive deterioration, while GBA1 mutation carriers also declined more rapidly albeit not significantly.
Conclusion: Understanding the genetic effects on survival and progression is crucial for patient counseling and inclusion in clinical trials.
© 2024 The Author(s). Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
References
-
- Shiner T, Mirelman A, Gana Weisz M, Bar‐Shira A, Ash E, Cialic R, et al. High frequency of GBA gene mutations in dementia with Lewy bodies among Ashkenazi Jews. JAMA Neurol 2016;73(12):1448–1453. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous