Clinical trial of arthroscopic debridement combined with functional exercise in the treatment of advanced knee osteoarthritis: A retrospective observational study
- PMID: 39213047
- PMCID: PMC11613048
- DOI: 10.3233/BMR-240106
Clinical trial of arthroscopic debridement combined with functional exercise in the treatment of advanced knee osteoarthritis: A retrospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Advanced knee osteoarthritis (KOA) impacts both knees, resulting in pain, deformity, and substantial restrictions in joint mobility.
Objective: This study aims to examine the effectiveness of combining arthroscopic debridement with functional exercise in treating advanced KOA.
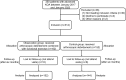
Methods: A total of 296 patients diagnosed with advanced KOA were divided into two groups: the observation group (n= 152) received arthroscopic debridement combined with functional exercise, while the control group (n= 144) underwent arthroscopic debridement only. The study compared and observed the outcomes between the two groups.
Results: There were no significant differences in knee joint function, inflammation level, and oxidative stress between the two groups before treatment (P> 0.05). Following treatment for six months, the observation group exhibited significantly lower visual analog scale (VAS) score, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels compared to the control group (P< 0.05). Meanwhile, the observation group showed significantly higher levels of Lysholm score, hospital for special surgery (HSS) score, range of motion (ROM) of knee, peak torque (PT) and total work (TW) for knee extension and flexion, superoxide dismutase (SOD), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and glutathione (GSH) compared to the control group (P< 0.05). Besides, the effective treatment rate in the observation group was notably higher than that in the control group (80.92% vs. 69.44%, P< 0.05).
Conclusion: The combination of arthroscopic debridement with functional exercise is an effective treatment for advanced KOA. This approach not only enhances the function and strength of knee joint and reduces inflammatory response but also boosts the body's antioxidant capacity. The treatment exhibits encouraging outcomes and warrants broad implementation.
Keywords: Advanced knee osteoarthritis; Arthroscopic debridement; Functional exercise; Retrospective observation; Therapeutic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Similar articles
-
[Case-controll study on the synergistic effects of electroacupuncture on knee osteoarthritis after arthroscopic debridement].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014 Apr;27(4):287-90. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014. PMID: 25029834 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of knee arthroscopic debridement combined with peripatellar denervation on restoration of knee function in patients with knee osteoarthritis.BMC Surg. 2023 Aug 11;23(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02113-4. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37568189 Free PMC article.
-
[Short-term effectiveness of joint distraction by Ilizarov combined with arthroscopic debridement in treatment of knee osteoarthritis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jul 15;31(7):794-798. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201701099. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29798521 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[The effect of arthroscopic debridement and conservative treatment in knee osteoarthritis: Results of a 5-year follow-up and literature review].Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2013 Dec;27(4):226-31. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1355854. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Sportverletz Sportschaden. 2013. PMID: 24198239 Review. German.
-
A meta-analysis and systematic review of the therapeutic effects of arthroscopy combined with intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Sep;10(9):9859-9869. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2145. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34628912
Cited by
-
Oxygen-ozone therapy for musculoskeletal pain in rehabilitation: Evidence and future perspectives.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(6):1423-1426. doi: 10.3233/BMR-245005. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 39546337 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kao MH, Tsai YF. Illness experiences in middle-aged adults with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: findings from a qualitative study. J Adv Nurs. 2014; 70(7): 1564-1572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous