Molecular recognition of an odorant by the murine trace amine-associated receptor TAAR7f
- PMID: 39215004
- PMCID: PMC11364543
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51793-w
Molecular recognition of an odorant by the murine trace amine-associated receptor TAAR7f
Abstract
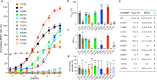
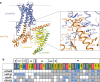
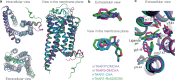
There are two main families of G protein-coupled receptors that detect odours in humans, the odorant receptors (ORs) and the trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs). Their amino acid sequences are distinct, with the TAARs being most similar to the aminergic receptors such as those activated by adrenaline, serotonin, dopamine and histamine. To elucidate the structural determinants of ligand recognition by TAARs, we have determined the cryo-EM structure of a murine receptor, mTAAR7f, coupled to the heterotrimeric G protein Gs and bound to the odorant N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine (DMCHA) to an overall resolution of 2.9 Å. DMCHA is bound in a hydrophobic orthosteric binding site primarily through van der Waals interactions and a strong charge-charge interaction between the tertiary amine of the ligand and an aspartic acid residue. This site is distinct and non-overlapping with the binding site for the odorant propionate in the odorant receptor OR51E2. The structure, in combination with mutagenesis data and molecular dynamics simulations suggests that the activation of the receptor follows a similar pathway to that of the β-adrenoceptors, with the significant difference that DMCHA interacts directly with one of the main activation microswitch residues, Trp6.48.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: C.G.T. is a shareholder, consultant and member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Sosei Heptares. Unique materials described in this paper are freely available upon reasonable request. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Molecular recognition of an aversive odorant by the murine trace amine-associated receptor TAAR7f.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 7:2023.07.07.547762. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.07.547762. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 30;15(1):7555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51793-w. PMID: 37461561 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Li, Q. & Liberles, S. D. Odor sensing by trace amine-associated receptors. in Chemosensory Transduction (eds. Zufall, F. & Munger, S. D.) 67–80 (Elsevier, 2016).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

