Replicability and generalizability in population psychiatric neuroimaging
- PMID: 39215207
- PMCID: PMC11526127
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-024-01960-w
Replicability and generalizability in population psychiatric neuroimaging
Erratum in
-
Correction: Neuropsychopharmacology Volume 50 Issue 1.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 May;50(6):1019-1020. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02087-2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40108440 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
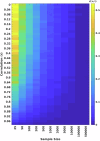
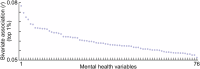
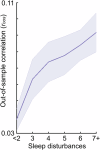
Studies linking mental health with brain function in cross-sectional population-based association studies have historically relied on small, underpowered samples. Given the small effect sizes typical of such brain-wide associations, studies require samples into the thousands to achieve the statistical power necessary for replicability. Here, we detail how small sample sizes have hampered replicability and provide sample size targets given established association strength benchmarks. Critically, while replicability will improve with larger samples, it is not guaranteed that observed effects will meaningfully apply to target populations of interest (i.e., be generalizable). We discuss important considerations related to generalizability in psychiatric neuroimaging and provide an example of generalizability failure due to "shortcut learning" in brain-based predictions of mental health phenotypes. Shortcut learning is a phenomenon whereby machine learning models learn an association between the brain and an unmeasured construct (the shortcut), rather than the intended target of mental health. Given the complex nature of brain-behavior interactions, the future of epidemiological approaches to brain-based studies of mental health will require large, diverse samples with comprehensive assessment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TOL holds a patent for taskless mapping of brain activity licensed to Sora Neurosciences and a patent for optimizing targets for neuromodulation, implant localization, and ablation is pending. TOL is a consultant for Turing Medical Inc. which commercializes Framewise Integrated Real-Time Motion Monitoring (FIRMM) software. These interests have been reviewed and managed by Washington University in St. Louis in accordance with its Conflict of Interest policies. Scott Marek declares no competing interest.
Figures
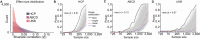
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

