Stable potassium isotope ratios in human blood serum towards biomarker development in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39217098
- PMCID: PMC11411773
- DOI: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfae038
Stable potassium isotope ratios in human blood serum towards biomarker development in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
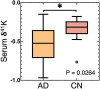
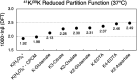
The Alzheimer's disease (AD)-affected brain purges K with concurrently increasing serum K, suggesting brain-blood K transferal. Here, natural stable K isotope ratios-δ41K-of human serum samples were characterized in an AD biomarker pilot study (plus two paired Li-heparin and potassium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [K-EDTA] plasma samples). AD serum was found to have a significantly lower mean δ41K relative to controls. To mechanistically explore this change, novel ab initio calculations (density functional theory) of relative K isotope compositions between hydrated K+ and organically bound K were performed, identifying hydrated K+ as isotopically light (lower δ41K) compared to organically bound K. Taken together with literature, serum δ41K and density functional theory results are consistent with efflux of hydrated K+ from the brain to the bloodstream, manifesting a measurable decrease in serum δ41K. These data introduce serum δ41K for further investigation as a minimally invasive AD biomarker, with cost, scalability, and stability advantages over current techniques.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; biomarker; isotope; metallomics; potassium.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
A.I.B. is a shareholder in Alterity Ltd. No further conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Roberts B. R., Doecke J. D., Rembach A., Yevenes L. F., Fowler C. J., McLean C. A., Lind M., Volitakis I., Masters C. L., Bush A. I., Hare D. J.; AIBL research group , Rubidium and potassium levels are altered in Alzheimer's disease brain and blood but not in cerebrospinal fluid, Acta Neuropathol. Commun., 2016, 4 (1), 119. 10.1186/s40478-016-0390-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Costas-Rodríguez M., Delanghe J., Vanhaecke F., High-precision isotopic analysis of essential mineral elements in biomedicine: natural isotope ratio variations as potential diagnostic and/or prognostic markers, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem., 2016, 76, 182–193. 10.1016/j.trac.2015.10.008 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

